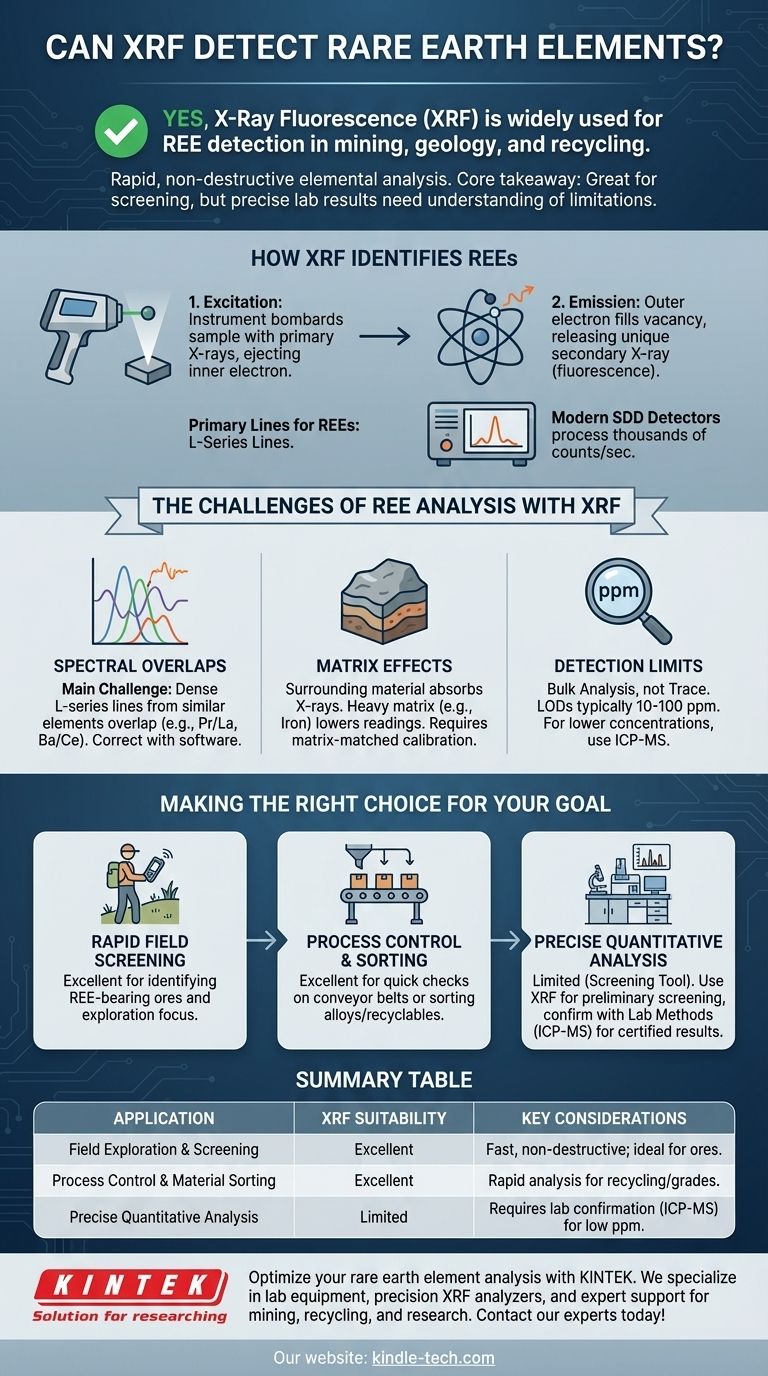
Ja, die Röntgenfluoreszenzanalyse (RFA) ist eine weit verbreitete und effektive Technologie zum Nachweis von Seltenen Erdmetallen (SEMs). Sie ist eine Standardmethode in der Bergbauforschung, Geologie und im Recycling, da sie eine schnelle, zerstörungsfreie Elementanalyse liefert. Die Effektivität und Genauigkeit der Analyse hängen jedoch stark von der Art des verwendeten RFA-Geräts, den spezifischen angestrebten SEMs und der Komplexität des gescannten Materials ab.
Die zentrale Erkenntnis ist, dass die RFA zwar ein unverzichtbares Werkzeug für das schnelle, semi-quantitative Screening von SEMs ist, aber um präzise Ergebnisse in Laborqualität zu erzielen, ist ein tiefes Verständnis ihrer inhärenten Einschränkungen – insbesondere spektraler Überlappungen und Matrixeffekte – erforderlich, was oft eine Bestätigung durch andere Analysemethoden notwendig macht.

Wie die RFA Seltene Erdmetalle identifiziert
Das Prinzip der Röntgenfluoreszenzanalyse
Im Kern ist die RFA-Analyse ein zweistufiger Prozess. Zuerst beschießt das Gerät eine Probe mit energiereichen Primär-Röntgenstrahlen. Diese Energie regt die Atome in der Probe an, wodurch sie ein Elektron aus einer inneren Schale ausstoßen.
Um Stabilität wiederzuerlangen, fällt sofort ein Elektron aus einer energiereicheren äußeren Schale nach, um die Lücke zu füllen. Dieser Übergang setzt eine spezifische Energiemenge in Form eines sekundären Röntgenstrahls frei, was die „Fluoreszenz“ ist, die der Detektor des Geräts misst.
Spektrale Signaturen von SEMs
Entscheidend ist, dass die Energie dieses sekundären Röntgenstrahls einzigartig für das Element ist, aus dem er emittiert wurde. Jedes Seltene Erdmetall besitzt einen charakteristischen „Fingerabdruck“ oder eine Signatur von Röntgenenergielinien.
Die primären Spektrallinien, die zur Identifizierung von SEMs verwendet werden, sind die L-Serienlinien. Dies liegt daran, dass die K-Serienlinien für diese schweren Elemente eine extrem hohe Anregungsenergie erfordern, die oft über die Fähigkeiten herkömmlicher RFA-Geräte hinausgeht.
Die Rolle moderner Detektoren
Moderne RFA-Analysatoren, insbesondere tragbare Geräte, verwenden hochentwickelte Silizium-Drift-Detektoren (SDDs). Diese Detektoren können Tausende von Röntgenstrahlzählungen pro Sekunde verarbeiten und verfügen über die Auflösung, um zwischen den oft dicht beieinander liegenden L-Serienlinien der verschiedenen SEMs unterscheiden zu können.
Die praktischen Herausforderungen der SEM-Analyse mit RFA
Obwohl das Prinzip einfach ist, stellt die reale SEM-Analyse erhebliche Herausforderungen dar, die Sie verstehen müssen, um Ihre Daten korrekt zu interpretieren.
Das Problem der spektralen Überlappungen
Dies ist die größte Herausforderung bei der RFA-Analyse von SEMs. Das Periodensystem ist in dieser Region dicht besiedelt, und ihre L-Serien-Emissionslinien sind zahlreich und oft sehr nah beieinander.
Dies führt zu erheblichen Peak-Überlappungen, bei denen das Signal eines Elements das Signal eines anderen stört oder fälschlicherweise dafür gehalten wird. Beispielsweise kann die Lα-Linie von Praseodym (Pr) mit der Lβ-Linie von Lanthan (La) überlappen, und Barium (Ba)-Linien können Cer (Ce) stören. Die Korrektur dieser Überlappungen erfordert hochentwickelte Software und eine sorgfältige Kalibrierung.
Leichte vs. Schwere SEMs
Die RFA ist im Allgemeinen empfindlicher für Schwere SEMs (HREEs) wie Gadolinium (Gd) und Yttrium (Y) als für Leichte SEMs (LREEs) wie Lanthan (La) und Cer (Ce).
Die von LREEs emittierten Röntgenstrahlen haben eine geringere Energie. Diese niederenergetischen Photonen werden leichter vom umgebenden Probenmaterial (der Matrix) und sogar von der Luft zwischen Probe und Detektor absorbiert, was ihr Signal abschwächt.
Matrixeffekte
Die Zusammensetzung des Materials, das die SEMs umgibt, hat einen großen Einfluss auf die Ergebnisse. Dies wird als Matrixeffekt bezeichnet.
Eine schwere Matrix, wie eine, die reich an Eisen oder Blei ist, kann die fluoreszierenden Röntgenstrahlen der SEMs absorbieren, was zu einer künstlich niedrigen Messung führt. Umgekehrt hat eine leichte Matrix, wie Siliziumdioxid, weniger Auswirkungen. Eine genaue Quantifizierung erfordert, dass Ihre Kalibrierstandards der Matrix Ihrer unbekannten Proben genau entsprechen.
Nachweisgrenzen
RFA ist eine Volumenanalysetechnik, keine Spurenanalysetechnik. Für SEMs liegen die Nachweisgrenzen (LODs) für tragbare RFA unter idealen Bedingungen typischerweise im Bereich von 10 bis 100 Teilen pro Million (ppm). Für die genaue Messung niedrigerer Konzentrationen müssen Sie auf laborbasierte Methoden wie ICP-MS zurückgreifen.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihr Ziel treffen
Der richtige Ansatz hängt vollständig von Ihrem Ziel ab. RFA ist keine Einzellösung, sondern ein vielseitiges Werkzeug mit unterschiedlichen Anwendungen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf schnellem Screening vor Ort oder geologischer Exploration liegt: Eine Handheld-RFA ist unübertroffen. Sie ermöglicht es Ihnen, SEM-haltige Erze zu identifizieren und sofort Entscheidungen darüber zu treffen, wo weitere Untersuchungen konzentriert werden sollen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf Prozesskontrolle oder Materialsortierung (z. B. Recycling) liegt: Handheld-RFA bietet die Geschwindigkeit, die erforderlich ist, um Materialqualitäten auf einem Förderband zu überprüfen oder Legierungen und Elektronikschrott, die SEMs enthalten, zu sortieren.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf präziser, quantitativer Analyse für Berichterstattung oder Forschung liegt: Verwenden Sie RFA als vorläufiges Screening-Tool, verlassen Sie sich jedoch für endgültige, zertifizierbare Ergebnisse, insbesondere bei niedrigen Konzentrationen, auf laborbasierte Methoden wie ICP-MS (Massenspektrometrie mit induktiv gekoppeltem Plasma).
Letztendlich bedeutet die effektive Nutzung der RFA für Seltene Erdmetalle, ihre Stärken in Bezug auf Geschwindigkeit und Zugänglichkeit zu nutzen und gleichzeitig ihre Grenzen in Bezug auf Präzision und Empfindlichkeit zu respektieren.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Anwendung | RFA-Eignung | Wichtige Überlegungen |
|---|---|---|
| Exploration & Screening vor Ort | Ausgezeichnet | Schnell, zerstörungsfrei; ideal zur Identifizierung von SEM-haltigen Erzen. |
| Prozesskontrolle & Materialsortierung | Ausgezeichnet | Schnelle Analyse für Recycling und Qualitätsprüfung. |
| Präzise quantitative Analyse | Begrenzt (Screening-Tool) | Erfordert Bestätigung durch Labormethoden wie ICP-MS bei niedrigen Konzentrationen. |
Optimieren Sie Ihre Analyse von Seltenen Erdmetallen mit der richtigen Ausrüstung. KINTEK ist spezialisiert auf Laborgeräte und Verbrauchsmaterialien und bedient Laboranforderungen mit präzisen RFA-Analysatoren und fachkundiger Unterstützung. Ob Sie in der Bergbauforschung, im Recycling oder in der Forschung tätig sind, unsere Lösungen liefern schnelle, zuverlässige Ergebnisse. Kontaktieren Sie noch heute unsere Experten, um das perfekte RFA-Werkzeug für Ihre spezifischen Herausforderungen bei der SEM-Detektion zu finden!
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- XRF Borsäure Labor Pulver Pellet Pressform für Laborgebrauch
- Labor-Kugelmahlanlage mit Aluminiumoxid-Zirkonoxid-Mahlbehälter und Kugeln
- Optisches Fensterglas Substratwafer Bariumfluorid BaF2 Substratfenster
- Optisches Fensterglas Substrat Wafer CaF2 Substrat Fenster Linse
- Assemble Lab Zylinderförmige Pressform
Andere fragen auch
- Was ist der Zweck der Verwendung einer Form beim Pelletpressen zur Vorbereitung von Katalysatortestproben? Sicherstellung der Datenkonsistenz
- Was sind die fünf wichtigsten Überlegungen bei der Gestaltung eines Probenvorbereitungsprotokolls für gepresste Pellets in der Röntgenfluoreszenzanalyse (RFA)?
- Wie bereitet man eine Probe für die RFA-Analyse vor? Meistern Sie die Schlüsselmethoden für genaue Ergebnisse
- Wie stellt man RFA-Pellets her? Eine 4-Schritte-Anleitung zur makellosen Probenvorbereitung
- Was sind die Proben für die RFA-Analyse? Ein Leitfaden zur Vorbereitung von Feststoffen, Pulvern und Flüssigkeiten


















