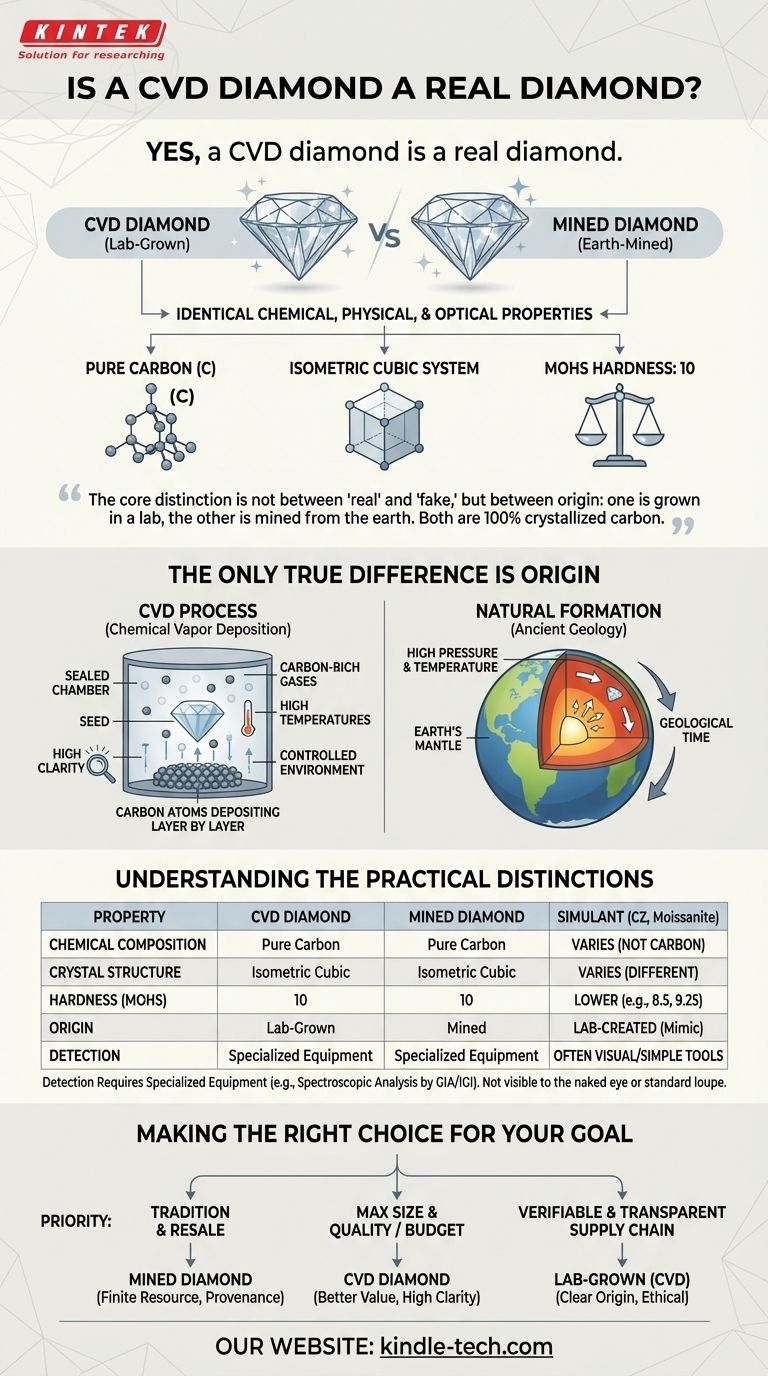
Ja, ein CVD-Diamant ist ein echter Diamant. Er besitzt exakt die gleichen chemischen, physikalischen und optischen Eigenschaften wie ein aus der Erde abgebauter Diamant. Beide bestehen aus reinem Kohlenstoff, der in einem isometrischen kubischen System kristallisiert ist, wodurch sie selbst für einen geschulten Juwelier ohne Spezialausrüstung nicht zu unterscheiden sind.
Der wesentliche Unterschied liegt nicht zwischen „echt“ und „gefälscht“, sondern in der Herkunft: Einer wird im Labor gezüchtet, der andere wird aus der Erde abgebaut. Beide sind zu 100 % kristalliner Kohlenstoff, genau wie Eis aus einem Gefrierschrank chemisch identisch mit Eis aus einem Gletscher ist.

Was definiert einen „echten“ Diamanten?
Um zu verstehen, warum ein CVD-Diamant als authentisch gilt, müssen wir zunächst definieren, was ein Diamant auf seiner fundamentalsten Ebene ist. Die Identität eines Diamanten wird durch seine Materialzusammensetzung und Struktur bestimmt, nicht durch seinen Ursprung.
Die Atomstruktur
Ein Diamant ist reiner Kohlenstoff, dessen Atome in einem bestimmten Kristallgitter angeordnet sind. Diese Struktur verleiht dem Diamanten seine unvergleichliche Härte und seine einzigartige Fähigkeit, mit Licht zu interagieren.
CVD-Diamanten werden aus einem Diamantensamen gezüchtet und teilen exakt diese Atomstruktur, was sie chemisch identisch mit ihren abgebauten Gegenstücken macht.
Identische physikalische und optische Eigenschaften
Da die chemische Zusammensetzung dieselbe ist, folgen alle anderen Eigenschaften. Ein CVD-Diamant weist das gleiche Feuer, die gleiche Brillanz und die gleiche Szintillation auf wie ein natürlicher Diamant.
Er erreicht außerdem die höchste Bewertung von 10 auf der Mohs-Härteskala, genau wie ein abgebauter Diamant.
Die offizielle Entscheidung
Die Debatte um die Terminologie wurde 2018 offiziell beigelegt. Die US-amerikanische Federal Trade Commission (FTC) entschied, dass ein Diamant unabhängig von seiner Herkunft ein Diamant ist.
Diese Entscheidung bestätigt rechtlich, dass im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten, einschließlich derer, die mittels des CVD-Verfahrens hergestellt wurden, keine Imitationen oder Fälschungen sind; sie sind lediglich Diamanten, die durch einen anderen Prozess entstanden sind.
Der einzige wahre Unterschied ist die Herkunft
Der einzige Faktor, der einen CVD-Diamanten von einem natürlichen unterscheidet, ist sein Entstehungsprozess. Einer ist ein Produkt moderner Technologie, während der andere ein Produkt alter Geologie ist.
Wie CVD-Diamanten hergestellt werden
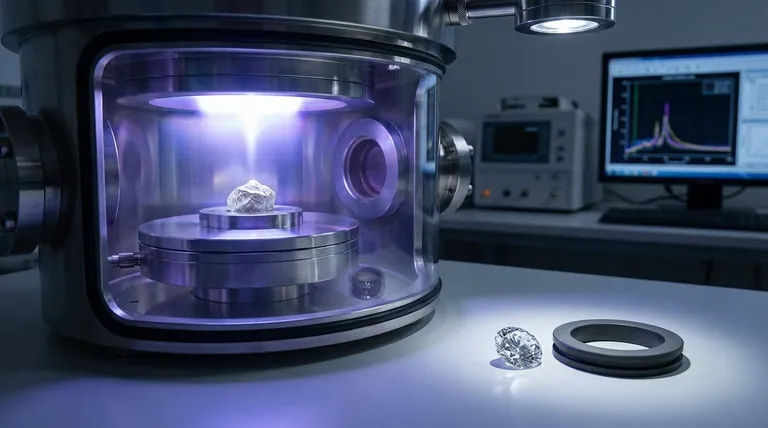
CVD steht für Chemical Vapor Deposition (Chemische Gasphasenabscheidung). Der Prozess beginnt mit einem dünnen Splitter eines Diamanten, bekannt als Samen. Dieser Samen wird in eine versiegelte Kammer gelegt, die mit kohlenstoffreichen Gasen gefüllt ist.
Die Kammer wird auf extreme Temperaturen erhitzt, wodurch die Gase zerfallen und Kohlenstoffatome auf dem Diamantsamen abgelagert werden, wodurch der Kristall Schicht für Schicht wächst.
Eine kontrollierte Umgebung
Da dieser Prozess unter hochkontrollierten und überwachten Bedingungen stattfindet, weisen CVD-Diamanten oft eine sehr hohe Reinheit und weniger Einschlüsse auf als viele natürliche Diamanten. Diese technologische Präzision ermöglicht die Herstellung von Steinen mit außergewöhnlicher Qualität.
Verständnis der praktischen Unterschiede
Obwohl sie physisch identisch sind, führen die unterschiedlichen Ursprünge von abgebauten und CVD-Diamanten zu einigen praktischen Überlegungen für den Käufer. Es ist entscheidend, sie von Diamantimitationen zu unterscheiden, bei denen es sich überhaupt nicht um echte Diamanten handelt.
Keine Imitation (wie Zirkonia oder Moissanit)
Ein häufiger Verwechslungspunkt ist der Vergleich von im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten mit Imitationen wie Zirkonia (CZ) oder Moissanit. Diese Materialien sind kein Kohlenstoff; sie ahmen nur das Aussehen eines Diamanten nach und weisen sehr unterschiedliche physikalische und chemische Eigenschaften auf.
Ein CVD-Diamant ist keine Imitation; er ist chemisch und strukturell ein Diamant.
Die Unterscheidung erfordert Spezialausrüstung
Sie können den Unterschied zwischen einem CVD- und einem abgebauten Diamanten nicht mit bloßem Auge oder einer normalen Juwelierlupe erkennen. Die Unterscheidung kann nur von einem geschulten Gemmologen mithilfe fortschrittlicher spektroskopischer Geräte getroffen werden.
Diese Geräte erkennen subtile Unterschiede in den Kristallwachstumsmustern und Spurenelementen, die auf eine im Labor gezüchtete Herkunft hinweisen. Deshalb sind offizielle Prüfberichte von Laboren wie GIA oder IGI unerlässlich.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihr Ziel treffen
Letztendlich hängt die Wahl zwischen einem CVD-Diamanten und einem abgebauten Diamanten von Ihren persönlichen Prioritäten und Werten ab. Beide sind authentische, schöne Optionen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf Tradition und potenziellem langfristigem Wiederverkaufswert liegt: Ein abgebauter Diamant mit starker Herkunftsnachweis könnte Ihre Präferenz sein, da es sich um eine endliche natürliche Ressource handelt.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk darauf liegt, Größe und Qualität für Ihr Budget zu maximieren: Ein CVD-Diamant ist die logische Wahl, da er ein deutlich besseres Preis-Leistungs-Verhältnis bietet.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf einer überprüfbaren und transparenten Lieferkette liegt: Ein im Labor gezüchteter Diamant bietet eine klare Herkunftsgeschichte, frei von den Unsicherheiten des Bergbaus.
Die Wahl eines CVD-Diamanten bedeutet, dass Sie sich für einen echten Diamanten entscheiden, der durch die Kraft der menschlichen Technologie und nicht durch Geologie entstanden ist.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Eigenschaft | CVD-Diamant | Abgebauter Diamant |
|---|---|---|
| Chemische Zusammensetzung | Reiner Kohlenstoff | Reiner Kohlenstoff |
| Kristallstruktur | Isometrisch kubisch | Isometrisch kubisch |
| Härte (Mohs-Skala) | 10 | 10 |
| Herkunft | Im Labor gezüchtet | Abgebaut |
Bereit, den perfekten Diamanten für Ihre Bedürfnisse zu finden? Ob Sie Wert auf außergewöhnliche Qualität, Wert oder eine transparente Lieferkette legen, die Expertise von KINTEK in fortschrittlichen Materialien kann Sie leiten. Als Spezialisten für Laborausrüstung und Verbrauchsmaterialien verstehen wir die Wissenschaft hinter der Herstellung makelloser Diamanten. Kontaktieren Sie noch heute unsere Experten, um Ihre spezifischen Anforderungen zu besprechen und herauszufinden, wie wir Sie mit Zuversicht und Klarheit auf Ihrem Weg unterstützen können.
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- Kundenspezifische CVD-Diamantbeschichtung für Laboranwendungen
- Zylindrischer Resonator MPCVD-Maschinensystemreaktor für Mikrowellen-Plasma-Chemische Gasphasenabscheidung und Labordiamantwachstum
- CVD-Diamantkuppeln für industrielle und wissenschaftliche Anwendungen
- CVD-Diamant-Schneidwerkzeugrohlinge für die Präzisionsbearbeitung
- CVD-Diamant-Optikfenster für Laboranwendungen
Andere fragen auch
- Wie werden Werkzeuge mit Diamant beschichtet? Erreichen Sie überlegene Härte und geringe Reibung für Ihre Werkzeuge
- Lohnt sich eine Diamantbeschichtung? Maximierung der Lebensdauer und Leistung von Komponenten
- Wie dick ist eine CVD-Diamantbeschichtung? Das Gleichgewicht zwischen Haltbarkeit und Spannung für optimale Leistung
- Was ist der Prozess der CVD-Diamantbeschichtung? Eine überlegene, chemisch gebundene Diamantschicht züchten
- Was sind diamantbeschichtete Filme? Veredelung von Materialien mit superharten, transparenten Schichten



















