Kurz gesagt: Die Eigenschaften einer Dünnschicht werden durch die Materialien, aus denen sie hergestellt wird, und, was noch wichtiger ist, durch den Abscheidungsprozess und die spezifischen Umgebungsbedingungen während ihrer Entstehung bestimmt. Faktoren wie die Substrattemperatur, die Energie der abscheidenden Teilchen und die Geometrie des Abscheidungssystems steuern direkt die endgültigen Eigenschaften der Schicht.
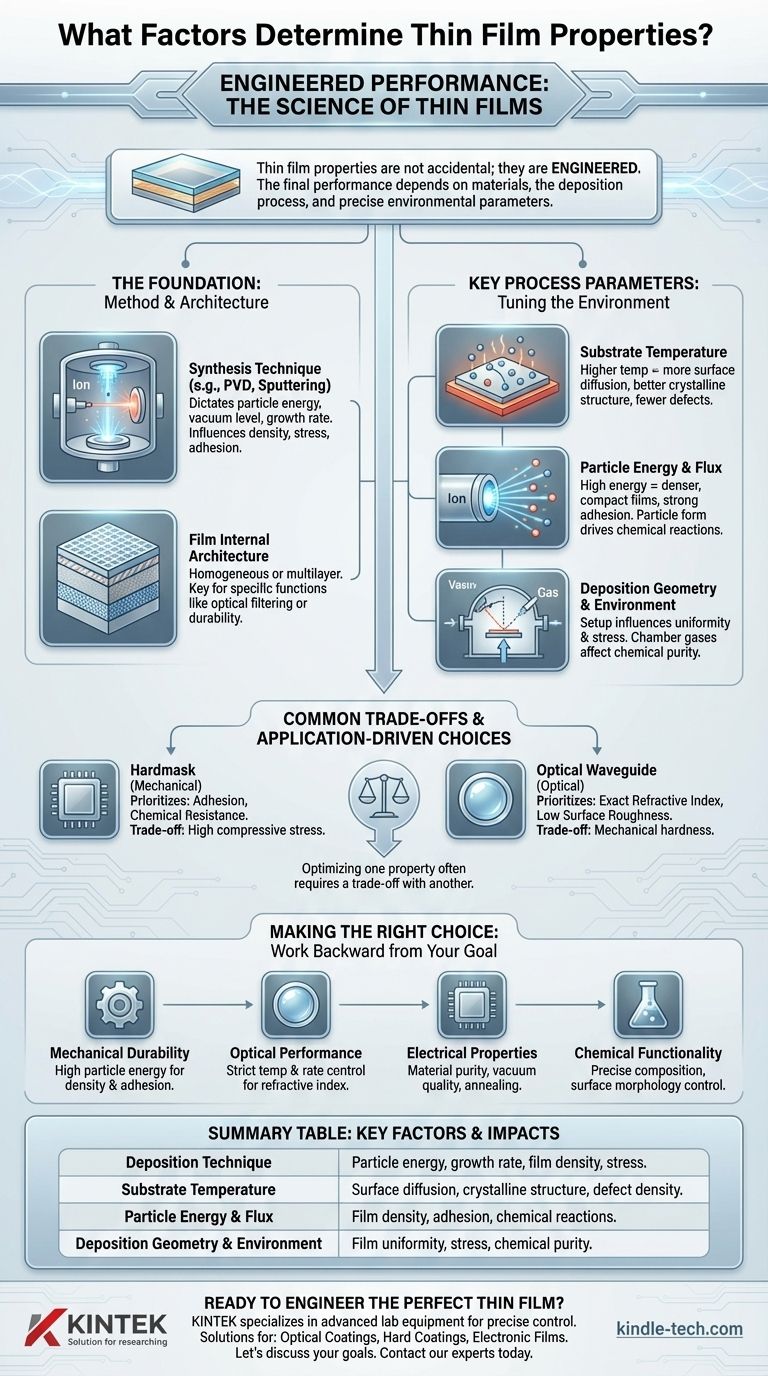
Das Kernprinzip, das es zu verstehen gilt, ist, dass die Eigenschaften einer Dünnschicht nicht zufällig sind; sie werden konstruiert. Die endgültige Leistung – sei sie optisch, mechanisch oder elektrisch – ist eine direkte Folge der präzisen und kontrollierbaren Bedingungen, unter denen die Schicht wächst.

Die Grundlage: Methode und Architektur
Bevor irgendein Prozess feinabgestimmt wird, sind die beiden grundlegendsten Entscheidungen, die Sie treffen werden, die Abscheidungstechnik und die beabsichtigte Struktur der Schicht. Diese Entscheidungen auf hoher Ebene legen die Grenzen für die erreichbaren Eigenschaften fest.
Auswahl der Synthesetechnik
Die Methode, die zur Herstellung der Schicht verwendet wird, ist ein Hauptfaktor. Techniken wie Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), Ionenstrahl-Sputtern oder Magnetronsputtern arbeiten alle unter unterschiedlichen physikalischen Prinzipien.
Diese Wahl bestimmt den Energiebereich der abscheidenden Teilchen, das erreichbare Vakuumniveau und die Wachstumsrate, was die Dichte, die Spannung und die Haftung der Schicht grundlegend beeinflusst.
Die innere Architektur der Schicht
Eine Dünnschicht ist nicht immer eine einzige, einheitliche Schicht. Ihre Eigenschaften hängen stark von ihrer konstruierten Struktur ab.
Es kann sich um eine homogene Einzelschicht mit gleichbleibender Zusammensetzung oder um eine komplexe inhomogene Mehrschichtstruktur handeln. Diese Architektur kann periodisch, gemustert oder zufällig sein und ist eine wichtige Designentscheidung, um spezifische Funktionen wie optische Filterung oder verbesserte Haltbarkeit zu erreichen.
Wichtige Prozessparameter, die Sie steuern können
Sobald eine Methode ausgewählt ist, werden die spezifischen Eigenschaften der Schicht durch die Manipulation der Parameter der Wachstumsumgebung abgestimmt. Diese Variablen geben Ihnen direkte Kontrolle über die resultierende Struktur und Leistung der Schicht.
Substrattemperatur
Die Temperatur der Oberfläche, auf der die Schicht wächst, ist eine der kritischsten Variablen.
Höhere Temperaturen liefern mehr Energie für die ankommenden Atome, wodurch sie sich auf der Oberfläche bewegen können (Oberflächendiffusion). Diese Mobilität hilft bei der Bildung geordneterer, kristalliner Strukturen und kann innere Spannungen und Defekte reduzieren.
Teilchenenergie und Fluss
Die Energie und die Rate (Fluss) der Atome oder Ionen, die auf dem Substrat ankommen, haben einen tiefgreifenden Einfluss auf die Dichte der Schicht.
Hochenergetische Teilchen, wie sie häufig bei Sputterprozessen vorkommen, können dichtere, kompaktere Schichten mit starker Haftung erzeugen. Die Form dieser Teilchen, wie bestimmte Radikale in einem Plasma, bestimmt auch die chemischen Reaktionen, die auf der wachsenden Oberfläche stattfinden.
Abscheidungsgeometrie und Umgebung
Der physikalische Aufbau der Abscheidungskammer, einschließlich des Abstands und Winkels zwischen der Materialquelle und dem Substrat (Streugeometrie), beeinflusst die Gleichmäßigkeit und die Spannung der Schicht.
Darüber hinaus können der Hintergrunddruck und die Zusammensetzung der Gase in der Kammer Verunreinigungen einführen oder an Reaktionen teilnehmen, wodurch sich die endgültigen chemischen und elektrischen Eigenschaften der Schicht ändern.
Häufige Kompromisse und anwendungsabhängige Entscheidungen
Es gibt nicht die eine „beste“ Dünnschicht; es gibt nur die richtige Schicht für eine bestimmte Anwendung. Das Verständnis dieses Kontexts ist entscheidend, da die Optimierung einer Eigenschaft oft einen Kompromiss mit einer anderen erfordert.
Eine Hartmaske im Vergleich zu einem optischen Wellenleiter
Die beabsichtigte Anwendung bestimmt vollständig, welche Eigenschaften wichtig sind.
Eine Schicht, die als Hartmaske für das Ätzen verwendet wird, erfordert ausgezeichnete Haftung und chemische Beständigkeit, benötigt jedoch möglicherweise keine spezifischen optischen oder elektrischen Eigenschaften. Umgekehrt erfordert eine Schicht für einen optischen Wellenleiter einen exakten Brechungsindex und minimale Oberflächenrauheit, während ihre mechanische Härte eine untergeordnete Rolle spielen kann.
Optimierung einer Eigenschaft auf Kosten einer anderen
Die Konstruktion einer Schicht ist ein Balanceakt. Prozesse, die extrem harte und dichte Beschichtungen erzeugen, tun dies oft, indem sie hohe Druckspannungen in der Schicht induzieren.
Diese hohe Spannung kann zwar für die Härte vorteilhaft sein, aber manchmal zu schlechter Haftung führen oder dazu, dass die Schicht reißt, insbesondere auf flexiblen Substraten. Sie müssen entscheiden, welche Eigenschaft für Ihr Ziel wichtiger ist.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihr Ziel treffen
Um eine Schicht effektiv zu konstruieren, müssen Sie rückwärts von Ihrem gewünschten Ergebnis arbeiten. Ihre primäre Anwendung bestimmt, welche Abscheidungsparameter priorisiert und gesteuert werden müssen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf mechanischer Haltbarkeit liegt (z. B. Hartbeschichtungen): Priorisieren Sie Abscheidungsmethoden, die eine hohe Teilchenenergie liefern, um die Schichtdichte und Haftung zu maximieren.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf präziser optischer Leistung liegt (z. B. Antireflexbeschichtungen): Konzentrieren Sie sich auf strenge Kontrolle der Substrattemperatur und der Abscheidungsrate, um den Brechungsindex fein abzustimmen und die Lichtstreuung durch Oberflächenrauheit zu minimieren.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf spezifischen elektrischen Eigenschaften liegt (z. B. Mikroelektronik): Achten Sie genau auf Materialreinheit, Vakuumqualität und die Wärmebehandlung nach der Abscheidung, um die kristalline Struktur und Reinheit der Schicht zu steuern.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf chemischer Funktionalität liegt (z. B. Sensoren oder Katalysatoren): Wählen Sie Methoden, die eine präzise Zusammensetzungskontrolle ermöglichen und eine spezifische Oberflächenmorphologie, wie z. B. eine hohe Porosität, erzeugen können.
Letztendlich ist die Herstellung einer Dünnschicht ein Akt bewusster Ingenieurskunst, bei dem jeder Parameter ein Hebel ist, um ein gewünschtes Ergebnis zu erzielen.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Wichtiger Faktor | Auswirkung auf die Eigenschaften der Dünnschicht |
|---|---|
| Abscheidungstechnik | Bestimmt Teilchenenergie, Wachstumsrate sowie erreichbare Schichtdichte und -spannung. |
| Substrattemperatur | Steuert die Oberflächendiffusion und beeinflusst so die Kristallstruktur und Defektdichte. |
| Teilchenenergie & Fluss | Beeinflusst die Schichtdichte, Haftung und die chemischen Reaktionen während des Wachstums. |
| Abscheidungsgeometrie & Umgebung | Beeinflusst die Gleichmäßigkeit und Spannung der Schicht sowie die chemische Reinheit. |
Bereit, die perfekte Dünnschicht für Ihre Anwendung zu entwickeln?
Die Eigenschaften Ihrer Dünnschicht – sei es für optische, mechanische oder elektrische Leistung – sind ein direktes Ergebnis des Abscheidungsprozesses. Bei KINTEK sind wir darauf spezialisiert, die fortschrittlichen Laborgeräte und die fachkundige Unterstützung bereitzustellen, die erforderlich sind, um diese kritischen Parameter präzise zu steuern.
Wir bedienen Labore, die sich auf Forschung & Entwicklung und Produktion konzentrieren, und bieten Lösungen für:
- Optische Beschichtungen: Erzielen Sie präzisen Brechungsindex und geringe Oberflächenrauheit.
- Hartbeschichtungen: Maximieren Sie Dichte und Haltbarkeit für anspruchsvolle Umgebungen.
- Elektronische Schichten: Gewährleisten Sie hohe Reinheit und spezifische Kristallstrukturen.
Lassen Sie uns Ihre spezifischen Ziele besprechen. Kontaktieren Sie noch heute unsere Experten, um die ideale Abscheidungslösung für Ihr Projekt zu finden.
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- RF PECVD System Hochfrequenz-Plasma-unterstützte chemische Gasphasenabscheidung RF PECVD
- Chemische Gasphasenabscheidung CVD-Anlagensystem Kammer-Schiebe-PECVD-Rohroofen mit Flüssigkeitsvergaser PECVD-Maschine
- Geteilter Kammer-CVD-Röhrenofen mit Vakuumpumpe, Anlage für chemische Gasphasenabscheidung
- Zylindrischer Resonator MPCVD-Maschinensystemreaktor für Mikrowellen-Plasma-Chemische Gasphasenabscheidung und Labordiamantwachstum
- Ölfreie Membran-Vakuumpumpe für Labor und Industrie
Andere fragen auch
- Was sind die Nachteile von PECVD? Die Abwägung bei der Niedertemperaturabscheidung verstehen
- Wie erzeugt Hochfrequenzleistung (HF) Plasma? Erreichen Sie stabiles Plasma mit hoher Dichte für Ihre Anwendungen
- Was ist Plasma-CVD? Erschließen Sie die Niedertemperatur-Dünnschichtabscheidung für empfindliche Materialien
- Warum wird bei PECVD häufig HF-Leistung verwendet? Für präzise Dünnschichtabscheidung bei niedriger Temperatur
- Wie unterscheiden sich PECVD und CVD? Ein Leitfaden zur Auswahl des richtigen Dünnschichtabscheidungsverfahrens


















