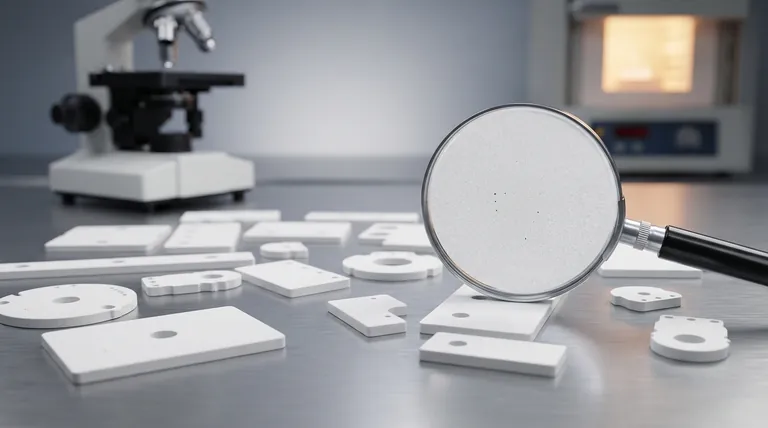
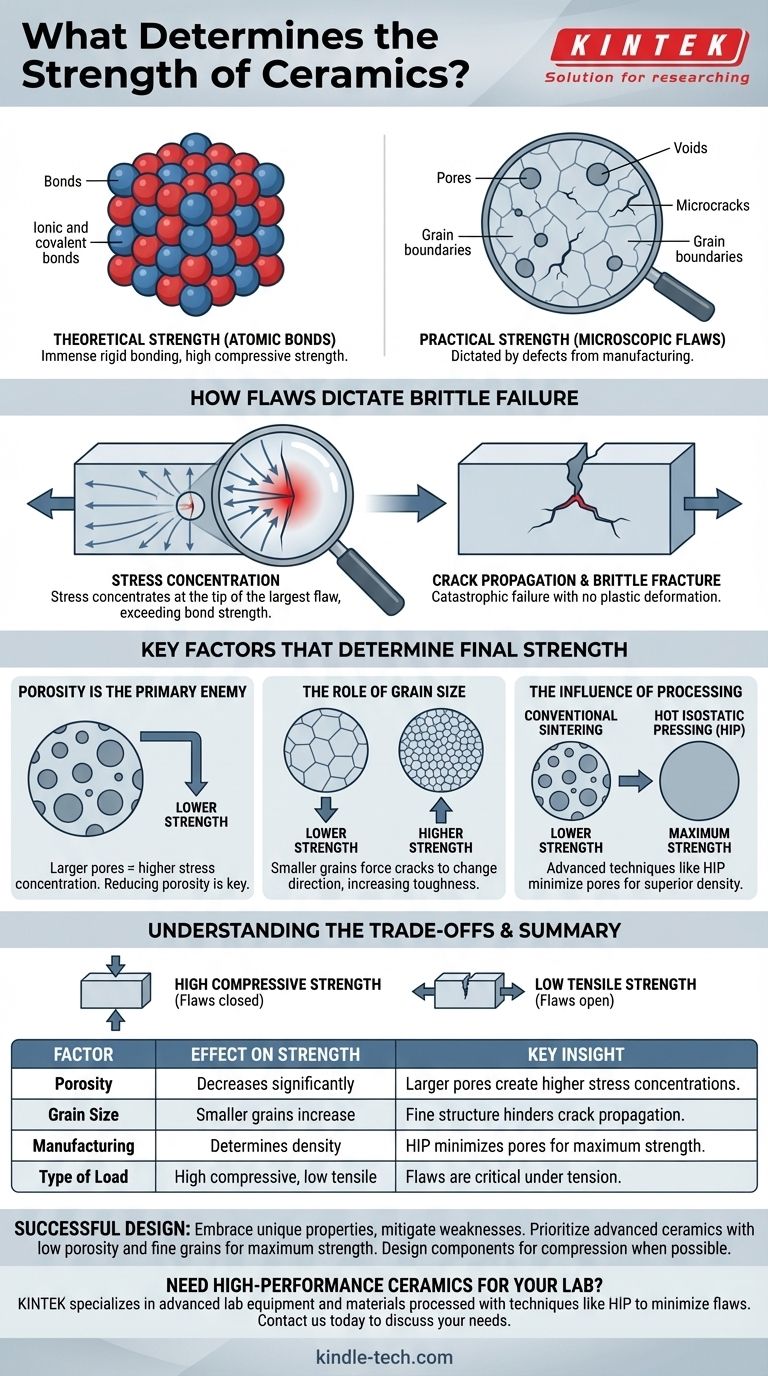
Letztendlich wird die Festigkeit einer Keramik nicht durch ihre starken atomaren Bindungen bestimmt, sondern durch die Anwesenheit und Größe ihrer mikroskopischen Defekte. Obwohl Keramiken aufgrund ihrer starren ionischen und kovalenten Bindungen eine immense theoretische Festigkeit aufweisen, wird ihre praktische, reale Festigkeit durch vorhandene Defekte wie Poren, Mikrorisse und Korngrenzen bestimmt, die während der Herstellung entstehen.
Das Kernprinzip, das es zu verstehen gilt, ist dieses: Die Festigkeit einer Keramik ist eine direkte Funktion ihrer Unvollkommenheiten. Spannungen konzentrieren sich an der Spitze des größten Defekts, und sobald diese Spannung die intrinsische Festigkeit des Materials übersteigt, breitet sich ein Riss katastrophal aus, was zu einem spröden Bruch führt.

Das Paradoxon: Immense Festigkeit durch Defekte untergraben
Keramiken stellen ein klassisches ingenieurtechnisches Paradoxon dar. Ihre innere Struktur ist unglaublich robust, dennoch können sie unter Bedingungen versagen, denen andere Materialien wie Metalle leicht standhalten würden. Dieses Verhalten wurzelt im Konflikt zwischen ihren atomaren Bindungen und ihrer Mikrostruktur.
Die Kraft der atomaren Bindungen
Keramiken zeichnen sich durch extrem starke und starre ionische und kovalente Bindungen aus. Diese Bindungen fixieren die Atome fest an ihrem Platz, weshalb Keramiken unglaublich hart, hochtemperaturbeständig und sehr druckfest (Widerstand gegen Zusammendrücken) sind.
Die unvermeidliche Realität der Defekte
Allerdings ist keine reale Keramik perfekt. Der Herstellungsprozess – das Mischen von Pulvern, das Formen und das Brennen bei hohen Temperaturen (Sintern) – erzeugt unweigerlich mikroskopische Defekte. Dazu gehören Poren (winzige Hohlräume), Mikrorisse und inkonsistente Korngrenzen.
Wie Defekte den spröden Bruch bestimmen
Diese winzigen, scheinbar unbedeutenden Defekte sind die wahren Bestimmungsfaktoren für die Festigkeit einer Keramik, wenn sie auseinandergezogen oder gebogen wird. Sie wirken als Ausgangspunkte für den Totalausfall.
Spannungskonzentration: Der Bruchpunkt
Wenn ein Keramikbauteil unter Zugspannung (einer ziehenden Kraft) steht, wird die Spannung nicht gleichmäßig verteilt. Stattdessen konzentriert sie sich intensiv an der scharfen Spitze des größten, schwerwiegendsten Defekts im Material.
Dieser Effekt vervielfacht die aufgebrachte Kraft an dieser einen Stelle. Eine mäßige äußere Last kann an einer Rissspitze eine massive lokale Spannung erzeugen, die die intrinsische Bindungsfestigkeit des Materials leicht übersteigt.
Rissausbreitung: Der Punkt ohne Wiederkehr
Bei Metallen würde diese hohe Spannung durch plastische Verformung abgebaut werden – das Material würde sich biegen und dehnen. Keramiken können dies nicht tun, da ihre starren Bindungen verhindern, dass Atome aneinander vorbeigleiten.
Stattdessen liefert die konzentrierte Spannung die Energie, um die atomaren Bindungen an der Rissspitze zu brechen, wodurch sich der Riss ausbreitet. Dieser Prozess nährt sich selbst, beschleunigt sich schnell durch das Material, bis es vollständig bricht – ein Phänomen, das als spröder Bruch bekannt ist.
Schlüsselfaktoren, die die Endfestigkeit bestimmen
Das Verständnis des Versagensmechanismus ermöglicht es uns, die kritischen Faktoren zu identifizieren, die die endgültige, nutzbare Festigkeit einer Keramikkomponente steuern.
Porosität ist der Hauptfeind
Der wichtigste Einzelfaktor ist die Porosität. Sowohl die Größe als auch die Menge der Poren wirken sich direkt auf die Festigkeit aus. Eine größere Pore erzeugt eine größere Spannungskonzentrationsstelle und macht sie so zum wahrscheinlichsten Fehlerpunkt. Die Reduzierung der Porosität ist der effektivste Weg, die Festigkeit einer Keramik zu verbessern.
Die Rolle der Korngröße
Die Festigkeit einer Keramik kann auch durch ihre Korngröße beeinflusst werden – die Größe der einzelnen kristallinen Bereiche innerhalb des Materials. Im Allgemeinen erhöht eine kleinere und gleichmäßigere Korngröße die Festigkeit und Zähigkeit. Ein Riss, der sich durch das Material ausbreitet, wird gezwungen, an jeder Korngrenze die Richtung zu ändern, was Energie verbraucht und den Bruch erschwert.
Der Einfluss der Verarbeitung
Die Herstellungsmethode steuert die Porosität und die Korngröße. Fortschrittliche Techniken wie Heißpressen oder Heißisostatisches Pressen (HIP) üben während des Brennens Druck aus, um Poren herauszupressen, was zu einem viel dichteren und festeren Endprodukt führt als beim herkömmlichen Sintern.
Die Abwägungen verstehen
Die inhärente Natur von Keramiken schafft eine Reihe von nicht verhandelbaren Kompromissen, die jeder Ingenieur berücksichtigen muss.
Hohe Druckfestigkeit vs. geringe Zugfestigkeit
Das definierende Merkmal von Keramiken ist ihre immense Festigkeit unter Druck, aber relative Schwäche unter Zug. Die Defekte, die unter Zugspannung den Bruch auslösen, werden unter Druck einfach zusammengedrückt, wodurch die starken atomaren Bindungen die Last tragen können.
Das Fehlen von „Zähigkeit“
Zähigkeit ist die Fähigkeit eines Materials, Energie zu absorbieren und sich vor dem Bruch zu verformen. Da Keramiken keinen Mechanismus für plastische Verformung besitzen, weisen sie eine sehr geringe Bruchzähigkeit auf. Das bedeutet, dass der Ausfall fast immer plötzlich, katastrophal und ohne Vorwarnung erfolgt.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihr Ziel treffen
Die spezifischen Anforderungen Ihrer Anwendung bestimmen, welche Keramikeigenschaften am wichtigsten sind.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf maximaler mechanischer Festigkeit liegt: Bevorzugen Sie fortschrittliche technische Keramiken mit dokumentiert geringer Porosität (<0,1 %) und feinen, kontrollierten Kornstrukturen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf thermischer Stabilität oder chemischer Beständigkeit liegt: Sie können oft konventionellere Keramiken verwenden, müssen aber Bauteile so konstruieren, dass sie unter Druck und niemals unter Zug belastet werden.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf Kosteneffizienz liegt: Akzeptieren Sie, dass traditionelle Keramiken eine höhere Porosität und geringere Festigkeit aufweisen, und entwerfen Sie eine dickere oder robustere Geometrie, um die Materialbeschränkungen auszugleichen.
Letztendlich beruht eine erfolgreiche Konstruktion mit Keramiken darauf, ihre einzigartigen Eigenschaften zu nutzen und ihre inhärenten Schwächen zu mildern.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Faktor | Auswirkung auf die Festigkeit | Wichtige Erkenntnis |
|---|---|---|
| Porosität | Verringert die Festigkeit erheblich | Größere Poren erzeugen höhere Spannungskonzentrationen, was den Ausfall wahrscheinlicher macht. |
| Korngröße | Kleinere Körner erhöhen die Festigkeit | Eine feine, gleichmäßige Kornstruktur zwingt Risse, die Richtung zu ändern, was die Ausbreitung behindert. |
| Herstellungsprozess | Bestimmt die endgültige Dichte und Defektgröße | Heißisostatisches Pressen (HIP) minimiert Poren für maximale Festigkeit. |
| Art der Belastung | Hohe Druckfestigkeit, geringe Zugfestigkeit | Defekte sind unter Zug kritisch, werden aber unter Druck geschlossen. |
Benötigen Sie Hochleistungskeramiken für Ihr Labor? Die Festigkeit und Zuverlässigkeit Ihrer Keramikkomponenten hängen direkt von ihrer Fertigungsqualität ab. Bei KINTEK sind wir auf fortschrittliche Laborgeräte und Verbrauchsmaterialien spezialisiert, einschließlich Materialien, die mit Techniken wie dem Heißisostatischen Pressen verarbeitet wurden, um Defekte zu minimieren und die Leistung zu maximieren. Lassen Sie sich von unseren Experten bei der Auswahl der richtigen Keramiklösung für Ihre spezifische Anwendung unterstützen – ob Sie maximale mechanische Festigkeit, thermische Stabilität oder chemische Beständigkeit benötigen.
Kontaktieren Sie uns noch heute, um zu besprechen, wie wir die Bedürfnisse Ihres Labors mit präzisionsgefertigten Keramiken unterstützen können.
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- Sonderform-Keramikplatten aus Aluminiumoxid-Zirkonoxid nach Maß für die Verarbeitung von fortschrittlicher Fein-Keramik
- Präzisionsgefertigte Zirkoniumdioxid-Keramikkugel für fortschrittliche Fein keramische Werkstoffe
- Technische Keramik Aluminiumoxid-Stab (Al2O3) Isoliert für industrielle Anwendungen
- Zirkonoxid-Keramikdichtung Technische Keramik
- Technische Pinzette aus fortschrittlicher Fein-Keramik mit Zirkonoxid-Keramikspitze und abgewinkeltem Ellbogen
Andere fragen auch
- Wie können verschiedene Materialien unterschiedliche Wärmekapazitäten haben? Die mikroskopischen Geheimnisse der Energiespeicherung entschlüsseln
- Welche Funktion erfüllen Aluminiumoxid-Keramikplatten als Träger bei der Herstellung von Molekularsiebmembranen?
- Was ist der Hauptunterschied zwischen Löten und Hartlöten? Wählen Sie die richtige Methode zur Metallverbindung
- Was sind die drei Arten von Beschichtungen? Ein Leitfaden für Architektur-, Industrie- und Spezialbeschichtungen
- Was ist der Unterschied zwischen metallischen und nicht-metallischen Beschichtungen? Ein Leitfaden zu Opfer- vs. Barriereschutz



















