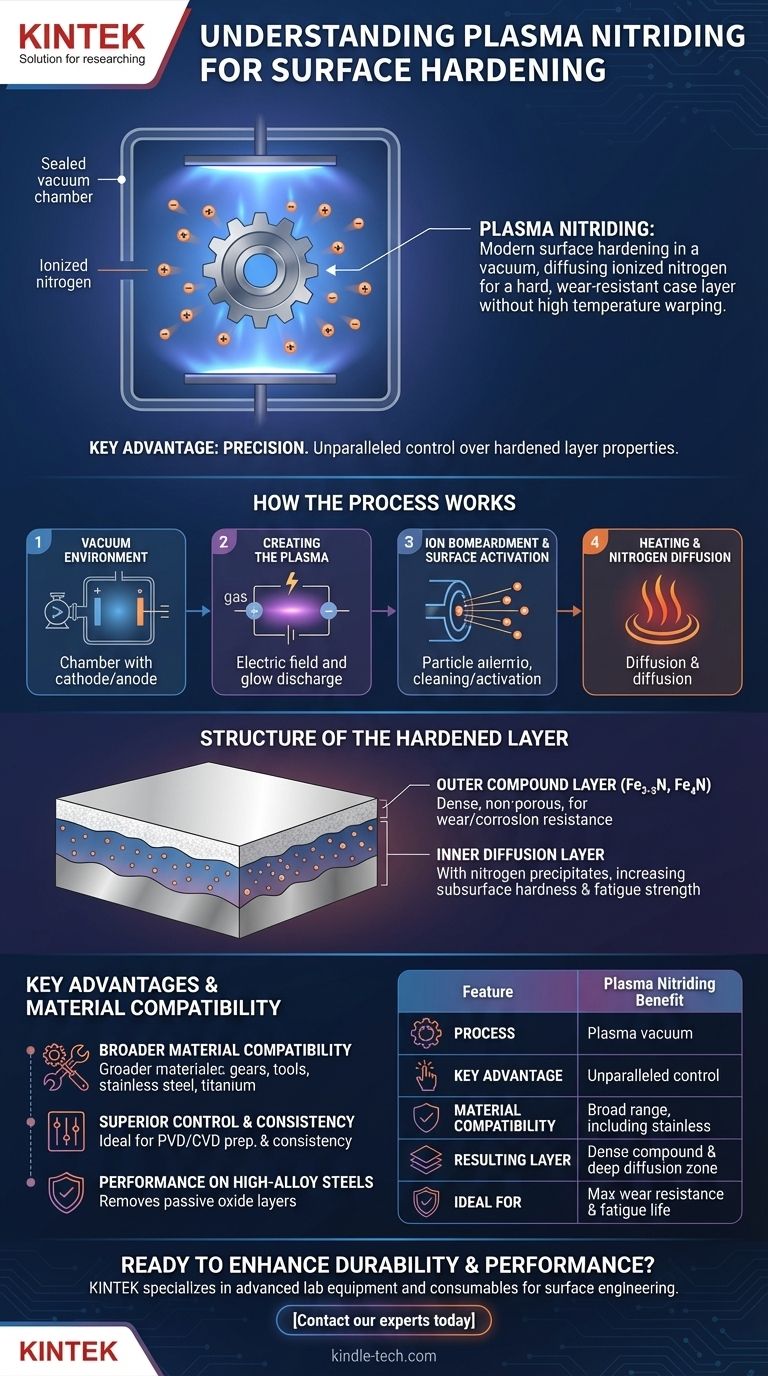
Kurz gesagt, Plasmanitrieren ist ein modernes Oberflächenhärteverfahren, das ionisiertes Stickstoffgas in einem Vakuum verwendet, um Stickstoff in die Oberfläche eines Metalls zu diffundieren. Dies erzeugt eine extrem harte und verschleißfeste Randschicht ohne die hohen Temperaturen oder das Abschrecken, die zu Verformungen von Bauteilen führen können.
Der entscheidende Vorteil des Plasmanitrierens liegt in seiner Präzision. Durch die Verwendung eines elektrischen Feldes zur Steuerung des Prozesses erhalten Ingenieure eine unvergleichliche Kontrolle über die Eigenschaften der gehärteten Schicht, was es für Hochleistungs- und empfindliche Komponenten traditionellen Methoden überlegen macht.
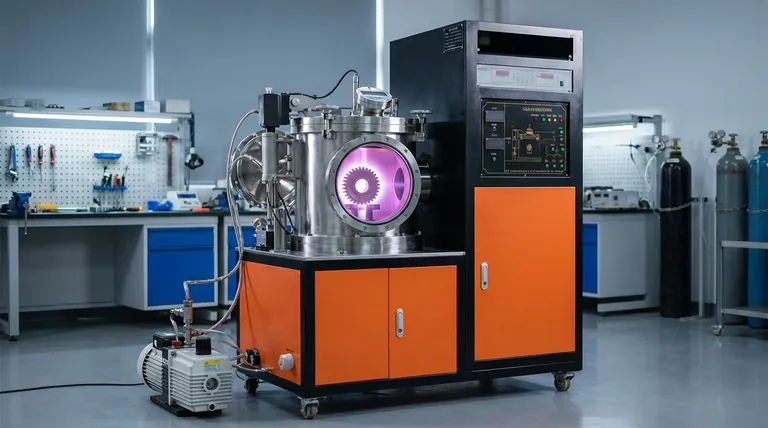

Wie der Plasmanitrierprozess funktioniert
Plasmanitrieren, auch als Ionen-Nitrieren bekannt, ist eine thermochemische Wärmebehandlung, die die Oberfläche eines Materials grundlegend verändert. Der Prozess findet vollständig in einer versiegelten Vakuumkammer statt.
Die Vakuumumgebung
Das zu behandelnde Werkstück wird in die Kammer gelegt und wird zur Kathode (negative Ladung). Die Ofenwand selbst fungiert als Anode (positive Ladung). Die Kammer wird dann evakuiert, um Verunreinigungen zu entfernen.
Erzeugung des Plasmas
Eine spezifische stickstoffbasierte Gasmischung wird in die Kammer eingeführt. Ein Hochspannungs-Elektrofeld wird zwischen dem Werkstück und der Ofenwand angelegt, wodurch das Gas ionisiert wird und ein niedrigdruckiges, leitfähiges Gas, bekannt als Plasma, bildet. Dies ist visuell als charakteristische Glimmentladung um das Bauteil herum erkennbar.
Ionenbeschuss und Oberflächenaktivierung
Die positiv geladenen Stickstoffionen innerhalb des Plasmas werden mit hoher Energie auf das negativ geladene Werkstück beschleunigt. Dieser Ionenbeschuss hat mehrere gleichzeitige Effekte.
Zunächst wird die Oberfläche auf mikroskopischer Ebene gesputtert, wodurch sie von Verunreinigungen gereinigt und passive Oxidschichten aufgelöst werden, was besonders kritisch für Edelstähle ist. Dies aktiviert die Oberfläche und macht sie sehr aufnahmefähig für Stickstoff.
Erwärmung und Stickstoffdiffusion
Der konstante Energietransfer durch den Ionenbeschuss erwärmt das Werkstück auch auf die erforderliche Nitriertemperatur. Sobald die Temperatur erreicht ist, ermöglicht die aktivierte Oberfläche leicht die Diffusion von Stickstoffatomen in das Material, wodurch der Härtungsprozess beginnt.
Die Struktur der gehärteten Schicht
Der Nitrierprozess erzeugt eine ausgeprägte, zweiteilige gehärtete Schicht auf der Materialoberfläche, jede mit einer spezifischen Funktion.
Die äußere Verbindungsschicht
Dies ist die äußerste Schicht, oft als "weiße Schicht" bezeichnet. Sie besteht aus harten Eisennitridverbindungen (ε-Nitrid Fe2-3N und γ'-Nitrid Fe4N). Beim Plasmanitrieren ist diese Schicht einzigartig dicht und porenfrei und bietet eine außergewöhnliche Beständigkeit gegen Verschleiß, Abrieb und Korrosion.
Die innere Diffusionsschicht
Unterhalb der Verbindungsschicht liegt die Diffusionsschicht. Hier ist Stickstoff tiefer in das Grundmaterial eingedrungen. Er bildet feine Ausscheidungen mit nitridbildenden Elementen in der Legierung (wie Chrom, Molybdän und Aluminium), wodurch die Untergrundhärte und die Ermüdungsfestigkeit des Bauteils erheblich erhöht werden.
Die wichtigsten Vorteile verstehen
Plasmanitrieren bietet erhebliche Vorteile gegenüber älteren Methoden wie Gas- oder Salzbadnitrieren, insbesondere für anspruchsvolle Anwendungen.
Breitere Materialkompatibilität
Das Verfahren ist für eine Vielzahl von Materialien wirksam. Dazu gehören alle Eisenmetalle, hochlegierte Werkzeugstähle, Gusseisen und sogar Materialien, die sonst schwer zu nitrieren sind, wie Edelstähle, Nickelbasislegierungen und Titanlegierungen.
Überragende Kontrolle und Konsistenz
Die elektrischen Parameter des Plasmas können präzise gesteuert werden. Dies ermöglicht eine Feinabstimmung der Struktur der nitrierten Schichten, z. B. die Erzeugung einer spezifischen Verbindungsschichtdicke oder sogar einer Schicht ohne Verbindungszone, was ideal für nachfolgende PVD- oder CVD-Beschichtungen ist.
Leistung bei hochlegierten Stählen
Bei hochlegierten und Edelstählen ist der Sputtereffekt des Plasmas entscheidend. Er entfernt effektiv die zähen, passiven Oxidschichten, die sonst die Stickstoffdiffusion verhindern würden, was zu einer viel härteren und konsistenteren Schicht führt, als dies beim Gasnitrieren möglich ist.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihr Ziel treffen
Das Verständnis dieser Prinzipien ermöglicht es Ihnen, die richtige Oberflächenbehandlung für Ihre spezifische technische Herausforderung auszuwählen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf maximaler Verschleiß- und Fressbeständigkeit liegt: Die dichte, porenfreie Verbindungsschicht, die durch Plasmanitrieren erzeugt wird, bietet überragende Leistung für Bauteile wie Zahnräder, Extruderschnecken und Gesenke.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Verbesserung der Ermüdungslebensdauer eines Bauteils liegt: Die tiefe Diffusionsschicht erhöht die Untergrundfestigkeit erheblich und ist daher ideal für Kurbelwellen, Nockenwellen und Achsen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Behandlung von Edelstahl oder hochlegiertem Werkzeugstahl liegt: Plasmanitrieren ist die definitive Wahl, da sein Oberflächenaktivierungsmechanismus die passiven Schichten überwindet, die diesen Materialien eigen sind.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Vorbereitung einer Oberfläche für eine Dünnschichtbeschichtung liegt: Die Fähigkeit, die Verbindungsschicht präzise zu steuern oder zu eliminieren, macht das Plasmanitrieren zu einem idealen vorbereitenden Schritt für PVD- und CVD-Prozesse.
Letztendlich ermöglicht die Nutzung des Plasmanitrierens ein Maß an Materialoberflächentechnik, das die Entwicklung langlebigerer, effizienterer und zuverlässigerer Bauteile ermöglicht.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Merkmal | Vorteil des Plasmanitrierens |
|---|---|
| Prozess | Verwendet ionisiertes Gas (Plasma) in einer Vakuumkammer |
| Hauptvorteil | Unvergleichliche Kontrolle über die Eigenschaften der gehärteten Schicht |
| Materialkompatibilität | Breite Palette, einschließlich Edelstähle & hochlegierte Werkzeugstähle |
| Resultierende Schicht | Dichte, porenfreie Verbindungsschicht und eine tiefe Diffusionszone |
| Ideal für | Bauteile, die maximale Verschleißfestigkeit und Ermüdungslebensdauer erfordern |
Bereit, die Haltbarkeit und Leistung Ihrer Komponenten zu verbessern?
KINTEK ist spezialisiert auf fortschrittliche Laborgeräte und Verbrauchsmaterialien für die Oberflächentechnik. Unsere Expertise in der Plasmanitriertechnologie kann Ihnen helfen, überragende Verschleißfestigkeit, Korrosionsschutz und eine verlängerte Ermüdungslebensdauer für Ihre Hochleistungsteile zu erzielen.
Kontaktieren Sie noch heute unsere Experten, um zu besprechen, wie Plasmanitrieren Ihre spezifischen Materialherausforderungen lösen und die Zuverlässigkeit Ihres Produkts verbessern kann.
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- Vakuum-Wärmebehandlungs- und Levitation-Induktionsschmelzofen
- Vakuumwärmebehandlungs- und Sinterofen mit 9 MPa Luftdruck
- Vakuum-Wärmebehandlungs-Sinter-Hartlöt-Ofen
- Vakuumwärmebehandlungsöfen mit Keramikfaser-Auskleidung
- Vakuumversiegelter kontinuierlich arbeitender Drehtiegelofen Rotierender Röhrenofen
Andere fragen auch
- Warum wärmebehandeln Sie im Vakuum? Erzielen Sie perfekte Oberflächengüte und Materialintegrität
- Was ist der Prozess des Vakuumhärtens? Überlegene Härte mit makelloser Oberflächengüte erzielen
- Welche verschiedenen Arten von Wärmebehandlungsverfahren gibt es für Stahl? Festigkeit, Härte und Zähigkeit maßschneidern
- Was ist ein Vakuum-Wärmebehandlungsofen? Der ultimative Leitfaden zur gesteuerten Atmosphäreverarbeitung
- Was sind die Bestandteile eines Vakuumofens? Ein Leitfaden zu den 5 Kernsystemen



















