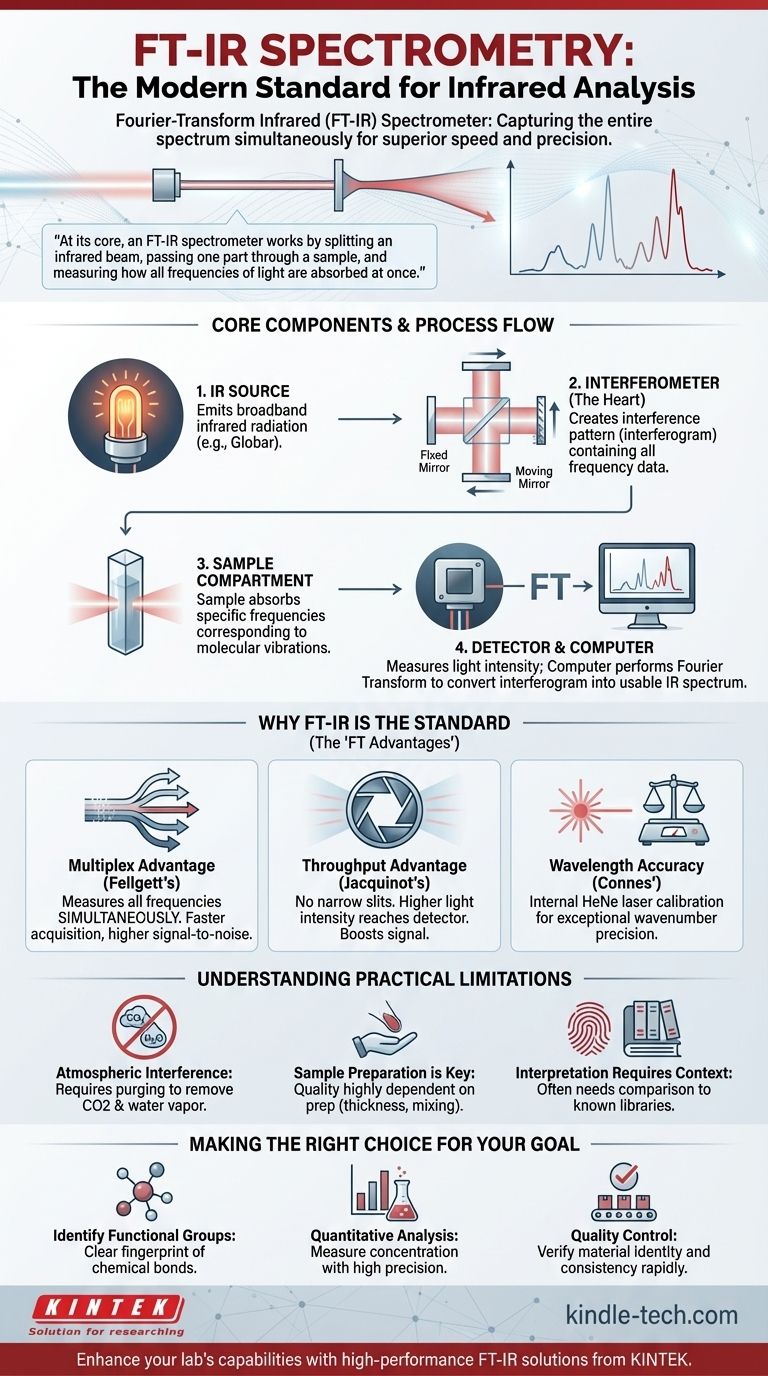
Das grundlegende Instrument für die moderne Infrarot(IR)-Spektrometrie ist das Fourier-Transform-Infrarot(FT-IR)-Spektrometer. Dieses Gerät ist zum Industrie- und Laborstandard geworden, da es das gesamte Infrarotspektrum einer Probe gleichzeitig erfasst. Dies wird erreicht, indem ein Interferenzmuster des Lichts gemessen und dann eine mathematische Operation, die Fourier-Transformation, verwendet wird, um dieses Muster in ein verwertbares Spektrum zu dekodieren.
Im Kern funktioniert ein FT-IR-Spektrometer, indem es einen Infrarotstrahl teilt, einen Teil durch eine Probe leitet und misst, wie alle Frequenzen des Lichts gleichzeitig absorbiert werden. Diese parallele Datenerfassung ist der Schlüssel zu seiner Geschwindigkeit, Empfindlichkeit und Präzision und macht es herkömmlichen, sequenziellen Methoden weit überlegen.
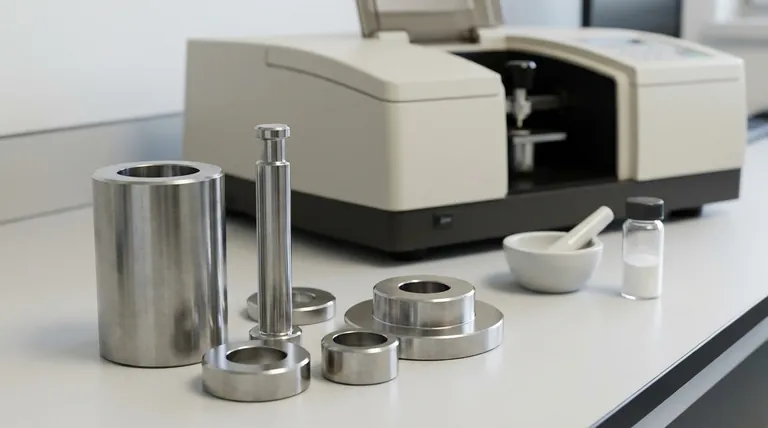

Die Kernkomponenten eines FT-IR-Spektrometers
Um zu verstehen, wie ein FT-IR-Spektrometer funktioniert, ist es wichtig, seine vier Hauptkomponenten zu kennen. Jede spielt eine eigenständige und entscheidende Rolle bei der Umwandlung einer physikalischen Probe in ein digitales Spektrum.
Die IR-Quelle
Der Prozess beginnt mit einer Quelle, die breitbandige Infrarotstrahlung emittiert. Dies ist typischerweise ein Keramikelement, wie ein Globar (Siliziumkarbid) oder ein Ever-Glo (proprietäres Material), das elektrisch erhitzt wird, um im Infrarotbereich hell zu leuchten und das für die Messung benötigte Licht bereitzustellen.
Das Interferometer (Das Herzstück des FT-IR)
Dies ist der innovativste Teil des Instruments. Es besteht aus einem Strahlteiler, einem festen Spiegel und einem beweglichen Spiegel. Der Strahlteiler teilt den IR-Strahl in zwei Teile, wobei einer zum festen Spiegel und der andere zum beweglichen Spiegel geleitet wird.
Wenn die beiden Strahlen zurückreflektiert werden, rekombinieren sie am Strahlteiler. Da der bewegliche Spiegel den Weg eines Strahls verändert hat, interferieren die Wellen miteinander. Dies erzeugt ein einzigartiges, komplexes Signal, das als Interferogramm bezeichnet wird und alle Frequenzinformationen auf einmal enthält.
Das Probenfach
Dies ist ein einfacher, aber kritischer Bereich, in dem die zu analysierende Probe platziert wird. Der vom Interferometer kommende, rekombinierte Infrarotstrahl durchdringt die Probe, die Licht bei bestimmten Frequenzen absorbiert, die den Schwingungen ihrer chemischen Bindungen entsprechen.
Der Detektor und der Computer
Ein Detektor, wie ein deuteriertes Triglycinsulfat (DTGS) oder ein Quecksilber-Cadmium-Tellurid (MCT)-Detektor, misst die Intensität des Lichts, das die Probe durchdringt. Er zeichnet das Interferogramm auf, eine Darstellung der Lichtintensität in Abhängigkeit von der Position des beweglichen Spiegels.
Dieses Rohsignal ist kein Spektrum. Der Computer des Instruments führt dann eine Fourier-Transformation durch, einen schnellen mathematischen Algorithmus, um das Interferogramm in das vertraute IR-Spektrum umzuwandeln: eine Darstellung von Absorption versus Wellenzahl (Frequenz).
Warum FT-IR der moderne Standard ist
Das FT-IR-Spektrometer hat ältere dispersive Instrumente aus mehreren wichtigen Gründen vollständig ersetzt, die oft als „FT-Vorteile“ bezeichnet werden.
Fellgetts Vorteil (Der Multiplex-Vorteil)
Ein FT-IR-Spektrometer misst alle Lichtfrequenzen gleichzeitig, anstatt sie einzeln zu durchlaufen. Dies ermöglicht die Erfassung eines vollständigen Spektrums in Sekunden und verbessert das Signal-Rausch-Verhältnis für eine gegebene Messzeit dramatisch.
Jacquinots Vorteil (Der Durchsatzvorteil)
Dispersive Instrumente benötigen schmale Spalte, um eine einzelne Wellenlänge auszuwählen, was den größten Teil des Lichts von der Quelle blockiert. Ein FT-IR hat solche Spalte nicht und ermöglicht es, dass eine viel höhere Lichtintensität (Durchsatz) den Detektor erreicht. Dies verbessert das Signal-Rausch-Verhältnis weiter.
Connes' Vorteil (Die Wellenlängen-Genauigkeit)
FT-IR-Spektrometer enthalten einen Helium-Neon (HeNe)-Laser als internen Wellenlängen-Kalibrierungsstandard. Das Instrument verwendet das präzise Einkanal-Signal des Lasers, um jederzeit die genaue Position des beweglichen Spiegels zu kennen, was zu einer außergewöhnlich hohen Genauigkeit und Präzision der Wellenzahl führt.
Verständnis der praktischen Einschränkungen
Obwohl es leistungsstark ist, ist ein FT-IR-Spektrometer keine magische Kiste. Eine objektive Analyse erfordert die Anerkennung seiner Grenzen.
Empfindlichkeit gegenüber atmosphärischen Störungen
Wasserdampf und Kohlendioxid in der Luft weisen starke Infrarotabsorptionen auf. Diese können sich mit dem Spektrum einer Probe überlagern und wichtige Peaks verdecken. Deshalb werden viele Geräte mit trockenem Stickstoff oder trockener Luft gespült, um atmosphärische Störungen zu beseitigen.
Die Probenvorbereitung ist entscheidend
Die Qualität eines IR-Spektrums hängt stark davon ab, wie die Probe vorbereitet wird. Eine zu dicke Probe absorbiert das gesamte Licht, während eine schlechte Durchmischung der Probe (wie bei einer KBr-Tablette) zu einem verzerrten Spektrum führt. Die Leistung des Instruments ist irrelevant, wenn die Probe falsch vorbereitet ist.
Die Interpretation erfordert Kontext
Ein IR-Spektrum ist ein molekularer „Fingerabdruck“. Es eignet sich hervorragend zur Identifizierung des Vorhandenseins spezifischer funktioneller Gruppen (z. B. C=O-, O-H-, N-H-Bindungen). Die Identifizierung eines vollständigen, unbekannten Moleküls erfordert jedoch oft den Vergleich des Spektrums mit einer Bibliothek bekannter Verbindungen oder die Verwendung ergänzender Analysetechniken.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihr Ziel treffen
Das Verständnis der Prinzipien des FT-IR ermöglicht es Ihnen, es effektiv für Ihre spezifische analytische Herausforderung einzusetzen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Identifizierung funktioneller Gruppen in einer Verbindung liegt: Das FT-IR ist Ihr ideales Werkzeug und liefert einen klaren und schnellen Fingerabdruck der vorhandenen chemischen Bindungen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der quantitativen Analyse liegt: Nutzen Sie die hohe Präzision und das Signal-Rausch-Verhältnis des FT-IR, um die Konzentration einer Komponente in einem Gemisch mithilfe des Lambert-Beerschen Gesetzes zu messen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Qualitätskontrolle liegt: Verwenden Sie das FT-IR, um das Spektrum einer Produktionsprobe schnell mit einem vertrauenswürdigen Referenzstandard zu vergleichen, um die Identität und Konsistenz des Materials zu überprüfen.
Durch das Verständnis seiner Kernkomponenten und Prinzipien wird das FT-IR-Spektrometer von einer komplexen Maschine zu einem intuitiven und leistungsstarken Werkzeug für die chemische Analyse.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Komponente | Funktion | Hauptmerkmal |
|---|---|---|
| IR-Quelle | Emittiert breitbandiges Infrarotlicht | Beheiztes Keramikelement (z. B. Globar) |
| Interferometer | Erzeugt ein Interferenzmuster (Interferogramm) | Strahlteiler, fester und beweglicher Spiegel |
| Probenfach | Hält die Probe zur Analyse | Licht passiert hindurch, spezifische Frequenzen werden absorbiert |
| Detektor & Computer | Misst die Lichtintensität und führt die Fourier-Transformation durch | Wandelt das Interferogramm in ein verwertbares Spektrum um |
Bereit, die analytischen Fähigkeiten Ihres Labors zu erweitern?
Ein FT-IR-Spektrometer ist ein Eckpfeiler für die Identifizierung funktioneller Gruppen, die Durchführung quantitativer Analysen und die Gewährleistung der Qualitätskontrolle. Bei KINTEK sind wir auf die Bereitstellung von Hochleistungs-Laborgeräten und Verbrauchsmaterialien spezialisiert, die auf Ihre spezifischen Forschungs- und Industrieanforderungen zugeschnitten sind.
Lassen Sie uns Ihnen helfen, präzise, zuverlässige Ergebnisse zu erzielen. Unsere Experten beraten Sie bei der idealen FT-IR-Lösung für Ihre Anwendung.
Kontaktieren Sie unser Team noch heute, um Ihre Anforderungen zu besprechen und den KINTEK-Unterschied zu entdecken!
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- XRF & KBR Stahlring Labor Pulver Pellet Pressform für FTIR
- Dreidimensionales elektromagnetisches Siebinstrument
- Elektrochemisches Laborarbeitsplatz-Potentiostat für Laboranwendungen
- Hochwiderstandsfähige Einkristall-Siliziumlinse für Infrarot
- CVD-Diamant-Optikfenster für Laboranwendungen
Andere fragen auch
- Welche Größenbereiche haben Pellets? Von 1 mm bis 25 mm – Finden Sie die perfekte Größe für Ihre Anwendung
- Was ist ein KBr-Pressling? Ein Leitfaden zur Herstellung fester Proben für die IR-Spektroskopie
- Wie führt man die KBr-Pressling-Methode durch? Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Anleitung zur perfekten FTIR-Probenvorbereitung
- Warum verwenden wir KBr-Presslinge in der IR-Spektroskopie? Ermöglichen Sie eine klare Probenanalyse mit einer infrarot-transparenten Matrix
- Warum wird KBr zur Herstellung der Tablette verwendet? Erzielen Sie klare, genaue IR-Spektroskopie-Ergebnisse



















