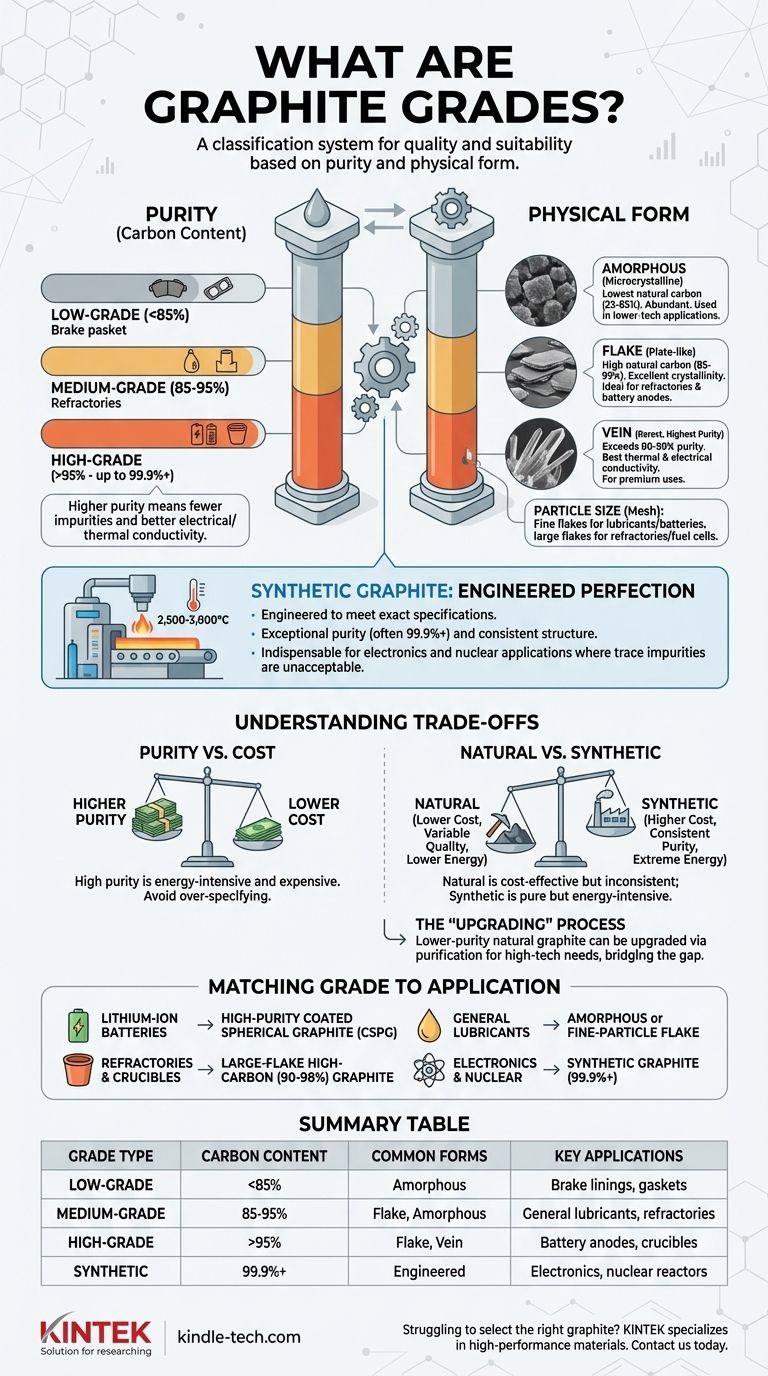
Graphitqualitäten sind ein Klassifizierungssystem, das zur Definition der Qualität und Eignung von Graphit für bestimmte industrielle Zwecke verwendet wird. Diese Qualitäten werden hauptsächlich durch zwei Schlüsselfaktoren bestimmt: Reinheit, gemessen als Kohlenstoffgehalt, und physikalische Form, die die Kristallinität und Partikelgröße des Materials umfasst. Dieses System ermöglicht es Ingenieuren und Herstellern, genau die Art von Graphit auszuwählen, die die Leistungs- und Kostenanforderungen ihrer Anwendung erfüllt.
Bei der Auswahl des richtigen Graphits geht es nicht darum, die „beste“ Qualität zu finden, sondern darum, die spezifischen Eigenschaften des Materials an die Anforderungen Ihres Projekts anzupassen. Die entscheidende Wahl hängt davon ab, das erforderliche Reinheitsniveau (Kohlenstoffgehalt) und die physikalische Form gegen die Gesamtkosten abzuwägen.
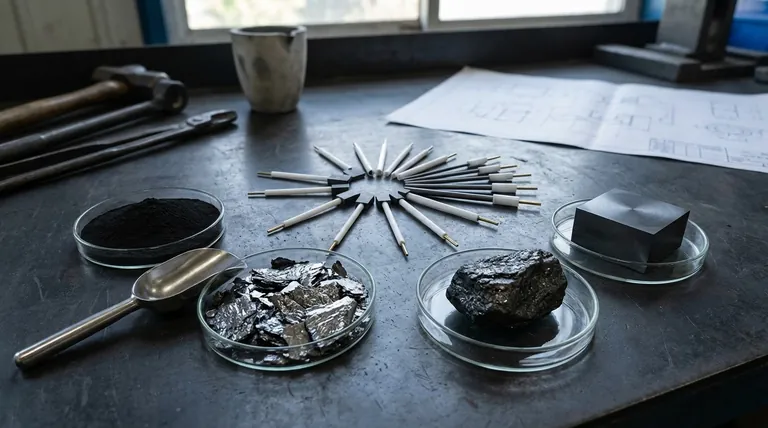

Die zwei Säulen der Graphitklassifizierung: Reinheit und Form
Der Wert und die Funktion von Graphit werden fast ausschließlich durch seine Reinheit und seine physikalische Struktur bestimmt. Diese beiden Eigenschaften bilden die Grundlage aller Klassifizierungssysteme.
Kohlenstoffgehalt: Die primäre Metrik der Reinheit
Die gebräuchlichste Methode zur Einstufung von Graphit ist sein Kohlenstoffgehalt. Je höher der Kohlenstoffanteil, desto geringer sind die Verunreinigungen (wie Asche, Kieselsäure oder andere Mineralien).
- Niedriggradiger Graphit: Enthält typischerweise weniger als 85 % Kohlenstoff. Er wird oft als amorpher Graphit bezeichnet.
- Mittelgradiger Graphit: Reicht von 85 % bis 95 % Kohlenstoff.
- Hochgradiger Graphit: Enthält über 95 % Kohlenstoff, wobei Spezialqualitäten für Anwendungen wie Batterien Reinheitsgrade von 99,9 % oder höher erreichen.
Höhere Reinheit korreliert direkt mit besserer elektrischer und thermischer Leitfähigkeit und ist daher für anspruchsvolle Anwendungen unerlässlich.
Physikalische Form: Das strukturelle Fundament
Natürlicher Graphit kommt in drei unterschiedlichen physikalischen Formen vor, die jeweils einzigartige Eigenschaften und Anwendungen aufweisen.
- Amorpher Graphit: Trotz seines Namens ist diese Form mikrokristallin. Er weist den niedrigsten natürlichen Kohlenstoffgehalt auf (typischerweise 25–85 %) und ist am häufigsten vorkommend. Er wird in Anwendungen mit geringerer Technologie wie Bremsbelägen, Dichtungen und Gießereiabdeckungen verwendet, bei denen hohe Reinheit nicht der Hauptfaktor ist.
- Flockengraphit: Diese Form besteht aus flachen, plattenartigen Partikeln. Er weist einen viel höheren natürlichen Kohlenstoffgehalt (85–99 %) und eine ausgezeichnete Kristallinität auf. Seine Struktur macht ihn ideal für feuerfeste Materialien (hohe Hitzebeständigkeit) und, was am wichtigsten ist, für die Anoden in Lithium-Ionen-Batterien, nachdem er zu sphärischem Graphit verarbeitet wurde.
- Adergraphit: Dies ist die seltenste und oft reinste Form von natürlichem Graphit, die in unterirdischen Adern vorkommt. Mit Reinheitsgraden, die oft 90–99 % übersteigen, weist er die beste thermische und elektrische Leitfähigkeit auf und ist somit ein Premium-Material für spezielle Schmierstoffe und Batteriekomponenten.
Die Rolle der Partikelgröße (Maschenweite)
Innerhalb jeder Güteklasse und Form ist die Partikelgröße ein entscheidender sekundärer Faktor. Gemessen in „Mesh“ (Maschenweite), bestimmt sie, wie sich der Graphit im Endprodukt verhält.
Große Flocken (+50 Mesh) sind wertvoller und werden für Anwendungen wie feuerfeste Materialien und Brennstoffzellen gesucht. Feinere Flocken (-100 Mesh) werden in Schmierstoffen, Beschichtungen und Batterieanoden verwendet.
Synthetischer Graphit: Eine eigene Klasse
Synthetischer Graphit wird nicht abgebaut, sondern ist ein technisches Produkt, das durch Erhitzen kohlenstoffhaltiger Materialien wie Petrolkoks auf extrem hohe Temperaturen (2.500–3.000 °C) hergestellt wird.
Der Fertigungsvorteil
Da er hergestellt wird, wird synthetischer Graphit nicht auf die gleiche Weise nach Reinheit eingestuft wie natürlicher Graphit. Stattdessen wird er von Grund auf so konstruiert, dass er exakte Spezifikationen erfüllt.
Reinheit und Konsistenz durch Design
Der Hauptvorteil von synthetischem Graphit ist seine außergewöhnliche Reinheit (oft 99,9 % oder höher) und seine hochgeordnete, konsistente Kristallstruktur. Dies macht ihn unverzichtbar für Anwendungen, bei denen selbst Spuren von Verunreinigungen inakzeptabel sind, wie z. B. in Kernreaktoren, der Halbleiterfertigung und bei Elektromotorkohlen.
Die Abwägungen verstehen
Die Auswahl der richtigen Graphitqualität erfordert ein klares Verständnis der Kompromisse zwischen Leistung, Kosten und Beschaffung.
Reinheit vs. Kosten
Dies ist der grundlegende Kompromiss. Die Erhöhung der Graphitreinheit ist ein energieintensiver und kostspieliger Prozess. Ein hochreiner Flockengraphit (99,9 %) kann ein Vielfaches eines Standardgrades (94 %) kosten. Die Verwendung einer Qualität mit höherer Reinheit als von der Anwendung gefordert, ist ein häufiger und kostspieliger Fehler.
Natürlich vs. Synthetisch
Natürlicher Graphit ist im Allgemeinen kostengünstiger und hat einen deutlich geringeren Energieaufwand bei der Erstproduktion. Seine Qualität kann jedoch inkonsistent sein.
Synthetischer Graphit bietet unübertroffene Reinheit und strukturelle Konsistenz, jedoch zu einem wesentlich höheren finanziellen und ökologischen Preis aufgrund der extremen Energie, die für seine Herstellung erforderlich ist.
Der „Aufwertungs“-Prozess
Natürlicher Graphit geringerer Reinheit wird oft „aufgewertet“, um den Anforderungen von Hochtechnologieanwendungen gerecht zu werden. Dies beinhaltet Reinigungsprozesse wie Flotation, chemische Wäsche oder thermische Behandlung. Dies erhöht die Kosten, wandelt jedoch ein Rohmaterial mit geringerem Wert in ein Hochleistungsprodukt um und schließt die Lücke zwischen natürlichem Angebot und industrieller Nachfrage.
Die Qualität an Ihre Anwendung anpassen
Verwenden Sie diese Richtlinien, um den geeigneten Graphit basierend auf Ihrem Hauptziel auszuwählen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf Lithium-Ionen-Batterien liegt: Sie benötigen hochreinen (99,95 %+), beschichteten sphärischen Graphit (CSPG), der aus hochgradigem Flockengraphit für optimale Anodenleistung gewonnen wird.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf feuerfesten Materialien und Tiegeln liegt: Sie benötigen großflockigen Graphit mit hohem Kohlenstoffgehalt (90–98 %) wegen seiner überlegenen thermischen Schockbeständigkeit und Nichtbenetzungseigenschaften.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf Schmierstoffen für allgemeine Zwecke liegt: Sie können amorphen Graphit geringerer Reinheit für grundlegende Bedürfnisse oder Flockengraphit mit feiner Partikelgröße für eine leistungsfähigere Schmierung verwenden.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf absoluter Reinheit für Elektronik- oder Nuklearanwendungen liegt: Sie müssen synthetischen Graphit wegen seiner konstruierten Konsistenz und seines nahezu perfekten Kohlenstoffgehalts spezifizieren.
Letztendlich geht es beim Verständnis von Graphitqualitäten darum, von einer einfachen „Gut gegen Schlecht“-Mentalität wegzukommen und einen präzisen, anwendungsorientierten Ansatz zur Materialauswahl zu verfolgen.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Qualitätstyp | Kohlenstoffgehalt | Häufige Formen | Wichtige Anwendungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Niedriggradig | < 85 % | Amorph | Bremsbeläge, Dichtungen |
| Mittelgradig | 85 % - 95 % | Flocke, Amorph | Allgemeine Schmierstoffe, feuerfeste Materialien |
| Hochgradig | > 95 % | Flocke, Ader | Batterieanoden, Tiegel |
| Synthetisch | 99,9 %+ | Konstruiert | Elektronik, Kernreaktoren |
Haben Sie Schwierigkeiten bei der Auswahl des richtigen Graphits für Ihr Labor oder Ihre Produktionsanforderungen? KINTEK ist spezialisiert auf Hochleistungslaborgeräte und Verbrauchsmaterialien, einschließlich präziser Graphitmaterialien für Anwendungen, die von der Batterieforschung bis zur Hochtemperaturverarbeitung reichen. Unsere Experten helfen Ihnen dabei, die perfekte Graphitqualität für Ihre spezifischen Anforderungen zu finden und so optimale Leistung und Kosteneffizienz zu gewährleisten. Kontaktieren Sie uns noch heute, um Ihr Projekt zu besprechen und herauszufinden, wie KINTEKs Lösungen die Fähigkeiten Ihres Labors verbessern können!
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- Graphit-Scheiben-Stab- und Plattenelektrode Elektrochemische Graphitelektrode
- Vertikaler Hochtemperatur-Graphit-Vakuum-Graphitierungs-Ofen
- Horizontaler Hochtemperatur-Graphit-Vakuum-Graphitierungs-Ofen
- Graphit-Vakuumofen mit Bodenentleerung für Kohlenstoffmaterialien
- Großer vertikaler Graphit-Vakuumgraphitierungs-Ofen
Andere fragen auch
- Was ist die Hauptfunktion von hochreinen Graphitelektroden bei der Wechselstromlaugung? Effiziente Metallrückgewinnung
- Welche technischen Vorteile bieten Kohlenstoff-Graphit-Elektroden für elektroaktive Biofilme? Optimieren Sie Ihre Bioforschung
- Welche potenziellen Risiken bestehen bei der Verwendung einer Graphitelektrode in elektrochemischen Tests? Vermeiden Sie Zersetzung und Kontamination
- Welche Eigenschaften haben Graphitstäbe? Nutzen Sie hohe Leitfähigkeit für extreme Anwendungen
- Warum wird ein hochreiner Graphitstab als Gegenelektrode für EIS ausgewählt? Sicherstellung der Datenintegrität und chemischen Stabilität



















