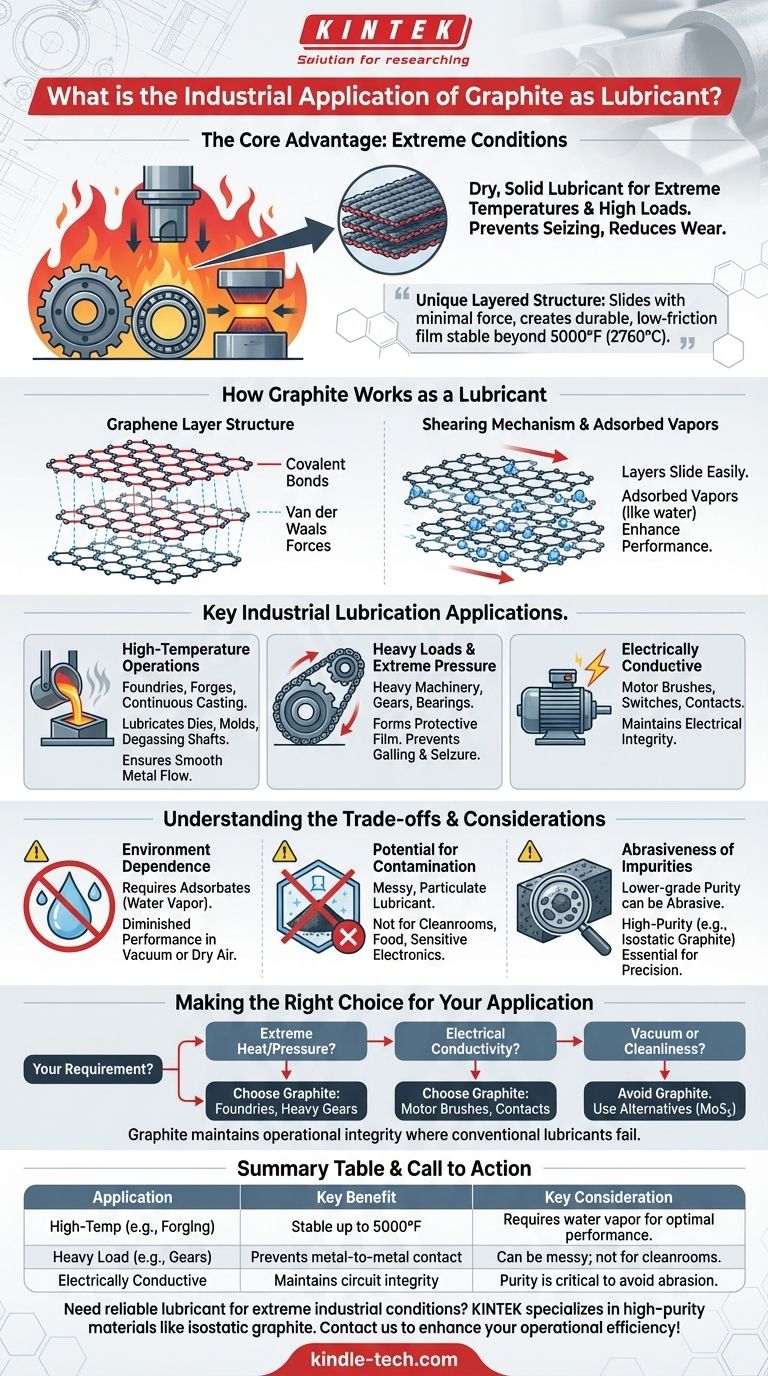
In industriellen Umgebungen wird Graphit als trockenes, festes Schmiermittel in Anwendungen eingesetzt, die extreme Temperaturen und hohe Lasten beinhalten, bei denen herkömmliche Öle und Fette zersetzt würden oder versagen. Es wird an Komponenten schwerer Maschinen wie Zahnrädern, Lagern und Gesenken in Branchen wie der Metallverarbeitung, dem Schmieden und dem Stranggießen verwendet, um Fressen zu verhindern und den Verschleiß zu reduzieren.
Der Hauptgrund, warum Graphit als Industrieschmiermittel hervorragend geeignet ist, liegt in seiner einzigartigen, geschichteten Kristallstruktur. Diese Schichten gleiten mit minimaler Kraft übereinander und bilden einen haltbaren, reibungsarmen Film, der selbst bei Temperaturen über 5000°F (2760°C) stabil bleibt.
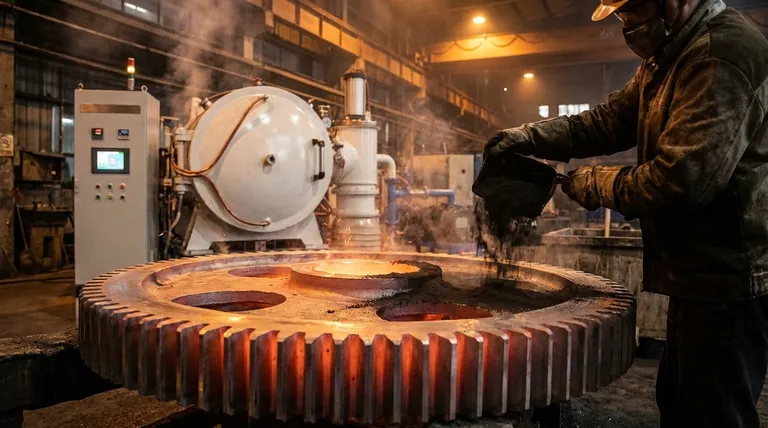

Wie Graphit als Schmiermittel wirkt
Die Graphen-Schichtstruktur
Graphit besteht aus gestapelten Schichten von Kohlenstoffatomen, bekannt als Graphenschichten. Innerhalb jeder Schicht sind die Kohlenstoffatome durch extrem starke kovalente Bindungen zusammengehalten.
Die Kräfte, die diese Schichten jedoch zusammenhalten, sind sehr schwache Van-der-Waals-Kräfte.
Der Scher-Mechanismus
Diese strukturelle Anordnung ist der Schlüssel zu seiner Schmiereigenschaft. Wenn eine Scherkraft ausgeübt wird, beispielsweise zwischen zwei beweglichen Maschinenteilen, brechen die schwachen Bindungen zwischen den Schichten leicht.
Dies ermöglicht es den Graphenschichten, mit sehr geringem Widerstand übereinander zu gleiten, ähnlich wie bei einem Kartenspiel, wodurch ein hochwirksamer Schmierfilm entsteht.
Die entscheidende Rolle adsorbierter Dämpfe
Damit Graphit seine geringste Reibung erreicht, ist es auf die Anwesenheit adsorbierter Dämpfe angewiesen, am häufigsten Wasserdampf aus der Luft.
Diese Moleküle gelangen zwischen die Graphitschichten und schwächen die Bindungen weiter ab, wodurch das Scheren und Gleiten der Schichten noch einfacher wird. Deshalb kann seine Leistung in einem Vakuum oder in extrem trockenen Umgebungen beeinträchtigt werden.
Wichtige industrielle Schmierungsanwendungen
Hochtemperaturbetrieb
Der bedeutendste Vorteil von Graphit ist seine thermische Stabilität. Es brennt, schmilzt oder zersetzt sich nicht bei den Betriebstemperaturen vieler industrieller Prozesse.
Es wird häufig in Gießereien und Schmieden zur Schmierung von Gesenken, Formen und Entgasungswellen eingesetzt. Beim Stranggießen sorgt es für den reibungslosen Fluss von geschmolzenem Metall, ohne dass es kleben bleibt.
Hohe Lasten und extremer Druck
Bei Maschinen mit großen Zahnrädern, Ketten und Lagern kann Graphit als trockenes Pulver oder als Zusatzstoff in Fetten verwendet werden.
Es bildet einen Schutzfilm, der enormem Druck standhält und direkten Metall-Metall-Kontakt, Kaltverschweißen und Fressen verhindert.
Elektrisch leitfähige Schmierung
Im Gegensatz zu den meisten Schmiermitteln ist Graphit ein ausgezeichneter elektrischer Leiter.
Diese einzigartige Eigenschaft macht es zum idealen Schmiermittel für Komponenten, die einen Stromkreis aufrechterhalten müssen, wie z. B. Motorkohlen, Schalter und elektrische Kontakte.
Die Kompromisse verstehen
Abhängigkeit von der Umgebung
Wie bereits erwähnt, hängt die Wirksamkeit von Graphit von der Anwesenheit von Adsorbaten wie Wasserdampf ab. Bei Anwendungen in großer Höhe oder im Vakuum nimmt seine Schmierfähigkeit erheblich ab, und es kann sogar abrasiv werden.
Potenzial für Kontamination
Als festes, partikuläres Schmiermittel kann Graphit unordentlich sein. Es ist nicht für Reinraumumgebungen, Lebensmittelverarbeitung oder empfindliche Elektronik geeignet, bei denen Partikelkontamination ein kritisches Problem darstellt.
Abrasivität von Verunreinigungen
Die Reinheit des Graphits ist entscheidend. Graphit von geringerer Qualität kann abrasive Verunreinigungen wie Kieselsäure enthalten, die zu Verschleiß und Beschädigung von Präzisionskomponenten führen können. Hochreine Qualitäten, wie isostatisches Graphit, sind für fortschrittliche und kritische Anwendungen erforderlich.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihre Anwendung treffen
Die Wahl des richtigen Schmiermittels ist eine entscheidende technische Entscheidung. Die einzigartigen Eigenschaften von Graphit machen es zu einem außergewöhnlichen Problemlöser für spezifische, herausfordernde Umgebungen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf extremer Hitze oder Druck liegt: Graphit ist oft die einzig gangbare Option zur Schmierung von Komponenten in Schmieden, Gießereien und hochbelasteten Getriebesystemen.
- Wenn Ihre Anwendung elektrische Leitfähigkeit erfordert: Graphit ist die Standardwahl für die Schmierung beweglicher elektrischer Teile wie Kommutatoren und Kontakte.
- Wenn Sie in einem Vakuum arbeiten oder extreme Sauberkeit benötigen: Sie sollten Graphit vermeiden und Alternativen wie Molybdändisulfid (MoS₂) oder andere Trockenfilmschmierstoffe in Betracht ziehen.
Letztendlich liegt der Wert von Graphit in seiner Fähigkeit, die Betriebsintegrität in Umgebungen aufrechtzuerhalten, in denen herkömmliche Schmiermittel einfach nicht überleben können.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Anwendung | Hauptvorteil | Wichtige Überlegung |
|---|---|---|
| Hochtemperaturbetrieb (z. B. Schmieden, Gießen) | Stabil bis 5000°F (2760°C) | Benötigt Wasserdampf für optimale Leistung |
| Hohe Last & extremer Druck (z. B. Zahnräder, Lager) | Verhindert Metall-Metall-Kontakt, Kaltverschweißen und Fressen | Kann unordentlich sein; nicht für Reinräume geeignet |
| Elektrisch leitfähige Schmierung (z. B. Motorkohlen) | Erhält die Schaltkreisintegrität bei gleichzeitiger Reduzierung der Reibung | Reinheit ist entscheidend, um abrasive Verunreinigungen zu vermeiden |
Benötigen Sie ein zuverlässiges Schmiermittel für extreme industrielle Bedingungen? Die Fähigkeit von Graphit, intensiver Hitze und Druck standzuhalten, macht es zu einer bevorzugten Lösung für anspruchsvolle Anwendungen in der Metallverarbeitung, im Schmieden und in elektrischen Systemen. Bei KINTEK sind wir auf hochreine Laborgeräte und Verbrauchsmaterialien spezialisiert, einschließlich fortschrittlicher Graphitmaterialien wie isostatischem Graphit, die auf kritische industrielle Anforderungen zugeschnitten sind. Lassen Sie sich von unseren Experten bei der Auswahl des richtigen Schmiermittels für Ihre Maschinen helfen – kontaktieren Sie uns noch heute, um Ihre Betriebsintegrität und Effizienz zu steigern!
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- Graphit-Vakuumwärmebehandlungsanlage mit 2200 °C
- Vertikaler Hochtemperatur-Graphit-Vakuum-Graphitierungs-Ofen
- Siliziummolydbid (MoSi2) Heizelemente für Elektroöfen
- Graphit-Vakuum-Durchlaufgraphitierungsöfen
- Graphitierungs-Vakuumofen für ultrahohe Temperaturen
Andere fragen auch
- Wie wirkt sich die Vakuumumgebung auf das Sintern von Diamant-Kupfer-Verbundwerkstoffen aus? Schutz vor thermischer Beschädigung
- Was ist der Zweck der Vakuumwärmebehandlung? Erzielung überlegener metallurgischer Reinheit und Leistung
- Was ist ein Vakuumofen? Der ultimative Leitfaden zur kontaminationsfreien thermischen Verarbeitung
- Was passiert mit der in einem Vakuum erzeugten Wärme? Beherrschen der thermischen Kontrolle für überlegene Materialien
- Warum sollte man Hartlöten anstelle von Löten wählen? Wegen überlegener Verbindungsfestigkeit und Hochtemperaturbeständigkeit


















