Elektronenstrahl-(E-Beam)-Verdampfung ist eine Hochvakuum-PVD-Technik (Physical Vapor Deposition), die zur Herstellung außergewöhnlich dünner und reiner Beschichtungen verwendet wird. Der Prozess nutzt einen fokussierten, hochenergetischen Elektronenstrahl, um ein Ausgangsmaterial zu erhitzen, wodurch es verdampft. Dieser Dampf bewegt sich dann in einer geraden Linie und kondensiert auf einem Substrat, wodurch ein präziser, Atom für Atom aufgebauter Film entsteht.
Die E-Beam-Beschichtung ist im Grunde ein Sichtlinien-Abscheidungsprozess, der für seine Präzision und geringe thermische Belastung des zu beschichtenden Bauteils geschätzt wird. Er eignet sich hervorragend zur Herstellung extrem reiner, dichter Filme für spezielle Anwendungen, aber seine gerichtete Natur stellt Herausforderungen bei der Beschichtung komplexer, dreidimensionaler Geometrien dar.

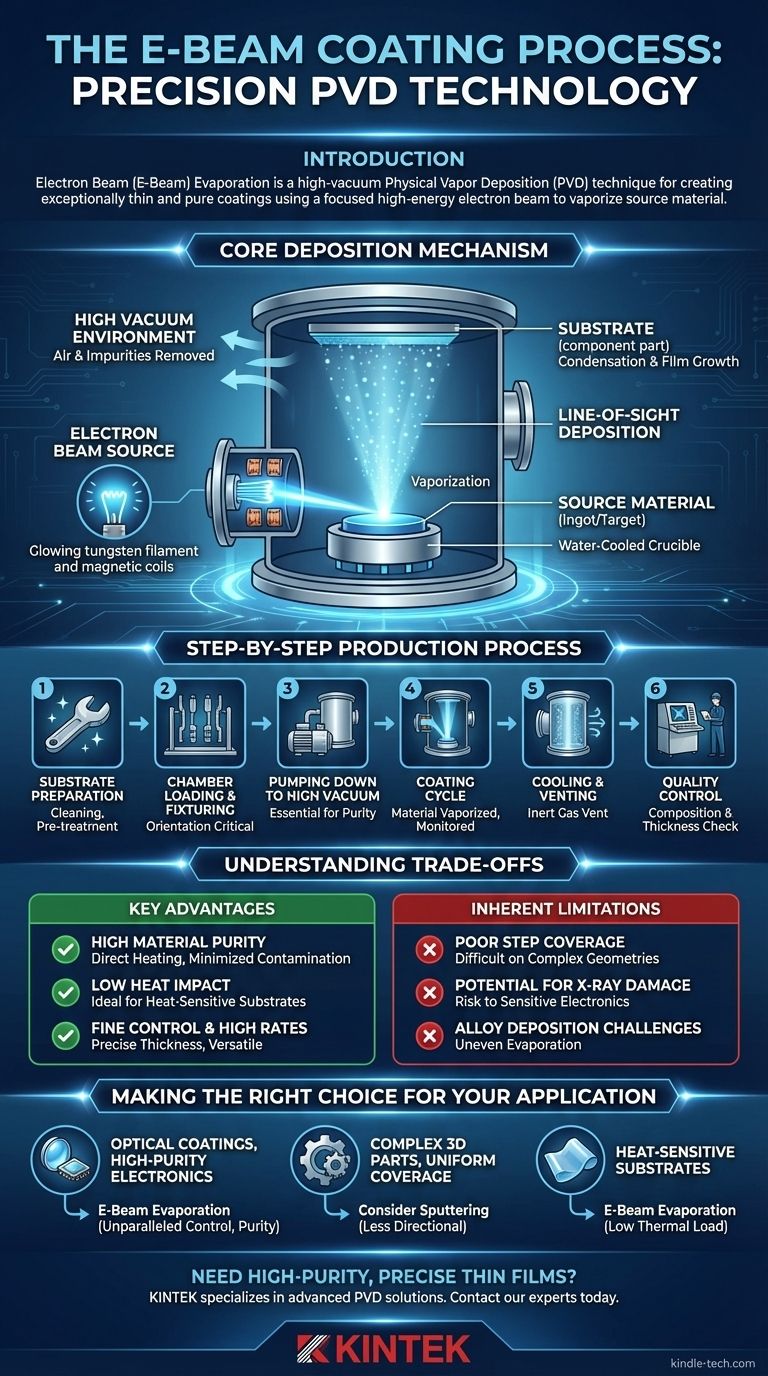
Der Kernmechanismus der Abscheidung
Um den E-Beam-Prozess zu verstehen, ist es wichtig, die grundlegende Physik zu erfassen, die in der Vakuumkammer stattfindet. Jeder Schritt wird präzise gesteuert, um eine bestimmte Filmzusammensetzung und -dicke zu erreichen.
Die Vakuumumgebung
Der gesamte Prozess findet in einer Hochvakuumkammer statt. Das Evakuieren der Kammer ist entscheidend, um Luft und andere gasförmige Verunreinigungen zu entfernen, die sonst mit dem verdampften Material reagieren und den endgültigen Film kontaminieren könnten. Dieser nahezu Vakuumzustand ermöglicht es den Dampfatomen auch, direkt zum Substrat zu gelangen, ohne mit anderen Partikeln zu kollidieren.
Die Elektronenstrahlquelle
Ein Wolframfaden wird erhitzt, um einen Elektronenstrom zu erzeugen. Diese Elektronen werden dann mit einer Reihe von Magnetfeldern beschleunigt und zu einem hochenergetischen Strahl fokussiert, ähnlich wie bei einem Kathodenstrahlröhren-Fernseher (CRT).
Verdampfen des Ausgangsmaterials
Dieser fokussierte Elektronenstrahl wird auf das Ausgangsmaterial (oft als Ingot oder Target bezeichnet) gerichtet, das in einem wassergekühlten Kupfertiegel gehalten wird. Die intensive Energie des Strahls erhitzt das Material bis zu seinem Siedepunkt, wodurch es verdampft oder sublimiert.
Sichtlinien-Abscheidung
Die Dampfatome bewegen sich auf einem geraden, direkten Weg von der Quelle zum Substrat. Diese "Sichtlinien"-Eigenschaft bedeutet, dass die Beschichtung nur auf Oberflächen abgeschieden wird, die direkt von der Verdampfungsquelle aus sichtbar sind.
Kondensation und Filmwachstum
Wenn die Dampfatome die vergleichsweise kühle Oberfläche des Substrats erreichen, kondensieren sie. Dieser Prozess baut die Beschichtung Schicht für Schicht, Atom für Atom auf, was zu einem sehr feinkörnigen und dichten Dünnfilm führt.
Der Schritt-für-Schritt-Produktionsprozess
Der Übergang vom Kernmechanismus zu einer industriellen Anwendung umfasst eine Reihe sorgfältig verwalteter Produktionsschritte.
Schritt 1: Substratvorbereitung
Eine ordnungsgemäße Haftung ist ohne eine makellose Oberfläche unmöglich. Dieser Schritt beinhaltet eine strenge Reinigung, um jegliche Verunreinigungen zu entfernen. Je nach Vorgeschichte des Teils kann dies auch das Entfernen alter Beschichtungen oder spezifische Vorbehandlungen zur Vorbereitung der Oberfläche umfassen.
Schritt 2: Kammerbeladung und Fixierung
Das Ausgangsmaterial wird in seinen Tiegel gelegt, und die Substrate werden auf spezielle Vorrichtungen oder Halterungen montiert. Die Ausrichtung dieser Vorrichtungen ist aufgrund der Sichtlinien-Natur des Prozesses entscheidend, um sicherzustellen, dass die Zieloberflächen dem Dampfstrom korrekt ausgesetzt sind.
Schritt 3: Evakuieren auf Hochvakuum
Nach dem Beladen wird die Kammer versiegelt und auf einen Zieldruck evakuiert. Dieses Abpumpen kann eine beträchtliche Zeit in Anspruch nehmen, ist aber für die Reinheit der endgültigen Beschichtung unerlässlich.
Schritt 4: Der Beschichtungszyklus
Nachdem das Vakuum hergestellt ist, wird der Elektronenstrahl aktiviert und das Material verdampft. Die Abscheidungsrate und die endgültige Dicke werden in Echtzeit überwacht, um sicherzustellen, dass der Film präzisen Spezifikationen entspricht. Der gesamte Zyklus kann je nach Material und gewünschter Dicke zwischen dreißig Minuten und mehreren Stunden dauern.
Schritt 5: Abkühlen und Entlüften
Nachdem die Zieldicke erreicht ist, wird der Elektronenstrahl deaktiviert. Das System darf abkühlen, bevor die Kammer mit einem Inertgas entlüftet und auf atmosphärischen Druck zurückgeführt wird.
Schritt 6: Qualitätskontrolle
Jede Charge wird einer strengen Inspektion unterzogen. Techniker verwenden Werkzeuge wie ein Röntgenfluoreszenz-(XRF)-Gerät, um die Zusammensetzung und Dicke der Beschichtung zu überprüfen und sicherzustellen, dass sie alle erforderlichen Standards erfüllt.
Die Kompromisse verstehen
Keine einzelne Beschichtungstechnologie ist perfekt für jede Anwendung. Die E-Beam-Verdampfung hat deutliche Vorteile und Einschränkungen, die ihre idealen Anwendungsfälle definieren.
Wesentliche Vorteile
- Hohe Materialreinheit: Der Elektronenstrahl erhitzt nur das Ausgangsmaterial direkt, nicht den gesamten Tiegel, wodurch Verunreinigungen minimiert werden und außergewöhnlich reine Filme entstehen.
- Geringe Wärmebelastung: Der Prozess überträgt im Vergleich zu anderen Methoden weniger Wärme auf das Substrat, wodurch er ideal für die Beschichtung hitzeempfindlicher Materialien wie Kunststoffe, Polymere oder vormontierte elektronische Komponenten ist.
- Feine Kontrolle & hohe Raten: Er ermöglicht eine sehr präzise Kontrolle über die Abscheidungsrate und Filmdicke und ist gleichzeitig in der Lage, sehr hohe Verdampfungsraten für eine Vielzahl von Materialien, einschließlich Metallen und Keramiken, zu erzielen.
Inhärente Einschränkungen
- Schlechte Stufenbedeckung: Der stark gerichtete Dampfstrom erschwert das gleichmäßige Beschichten komplexer Formen, scharfer Kanten oder Innenflächen. Er beschichtet hauptsächlich das, was er "sehen" kann.
- Potenzielles Röntgenstrahlschäden: Die Wechselwirkung hochenergetischer Elektronen mit dem Ausgangsmaterial kann Röntgenstrahlen erzeugen. Obwohl typischerweise auf niedrigem Niveau, können diese ausreichen, um hochsensible elektronische Substrate oder optische Komponenten zu beschädigen.
- Herausforderungen bei der Legierungsabscheidung: Es kann schwierig sein, Materialien aus mehreren Elementen (Legierungen) mit unterschiedlichen Dampfdrücken zu verdampfen, da das flüchtigere Element zuerst verdampft.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihre Anwendung treffen
Die Auswahl der richtigen PVD-Methode erfordert die Abstimmung der Prozessfähigkeiten mit Ihrem primären technischen Ziel.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf optischen Beschichtungen oder hochreiner Elektronik liegt: Die E-Beam-Verdampfung bietet eine unübertroffene Kontrolle über Filmdicke, Reinheit und Dichte, was für diese Anwendungen entscheidend ist.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Beschichtung komplexer 3D-Teile mit gleichmäßiger Abdeckung liegt: Sie sollten weniger gerichtete PVD-Methoden wie das Sputtern in Betracht ziehen, um sicherzustellen, dass alle Oberflächen ausreichend beschichtet werden.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Beschichtung hitzeempfindlicher Substrate liegt: Die geringe thermische Belastung des E-Beam-Prozesses macht ihn zu einer überlegenen Wahl zum Schutz von Materialien wie Polymeren oder empfindlichen, vormontierten Komponenten.
Letztendlich ist die Wahl der E-Beam-Verdampfung eine strategische Entscheidung für Anwendungen, bei denen die Qualität und Präzision des Endfilms wichtiger sind als eine gleichmäßige geometrische Abdeckung.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Schlüsselaspekt | Details |
|---|---|
| Prozesstyp | Physikalische Gasphasenabscheidung (PVD) |
| Umgebung | Hochvakuum |
| Mechanismus | Sichtlinien-Abscheidung |
| Wesentliche Vorteile | Hohe Reinheit, geringe thermische Belastung, präzise Dickenkontrolle |
| Ideal für | Optische Beschichtungen, hochreine Elektronik, hitzeempfindliche Substrate |
| Einschränkungen | Schlechte Abdeckung bei komplexen 3D-Geometrien |
Benötigen Sie hochreine, präzise Dünnschichten für Ihre Forschung oder Produktion?
KINTEK ist spezialisiert auf fortschrittliche Laborausrüstung, einschließlich PVD-Lösungen für anspruchsvolle Anwendungen. Unser Fachwissen kann Ihnen helfen, die richtige Beschichtungstechnologie auszuwählen, um eine überragende Filmqualität, Reinheit und Leistung für Ihre spezifischen Substrate und Ziele zu gewährleisten.
Kontaktieren Sie noch heute unsere Experten, um zu besprechen, wie wir die Dünnschichtabscheidungsbedürfnisse Ihres Labors unterstützen können.
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- RF PECVD System Hochfrequenz-Plasma-unterstützte chemische Gasphasenabscheidung RF PECVD
- Elektronenstrahlverdampfung Beschichtung Leitfähiger Bornitrid Tiegel BN Tiegel
- Molybdän-Wolfram-Tantal-Verdampfungsschiffchen für Hochtemperaturanwendungen
- Chemische Gasphasenabscheidung CVD-Anlagensystem Kammer-Schiebe-PECVD-Rohroofen mit Flüssigkeitsvergaser PECVD-Maschine
- Halbkugelförmiges Bodentiegel aus Wolfram für Verdampfung
Andere fragen auch
- Wie erzeugt Hochfrequenzleistung (HF) Plasma? Erreichen Sie stabiles Plasma mit hoher Dichte für Ihre Anwendungen
- Warum wird bei PECVD häufig HF-Leistung verwendet? Für präzise Dünnschichtabscheidung bei niedriger Temperatur
- Was sind die Anwendungen von PECVD? Essentiell für Halbleiter, MEMS und Solarzellen
- Was bedeutet plasmaunterstützt? Ein Leitfaden für Niedertemperatur-, Hochpräzisionsfertigung
- Was ist die Plasma-aktivierte chemische Gasphasenabscheidung? Eine Niedertemperaturlösung für fortschrittliche Beschichtungen



















