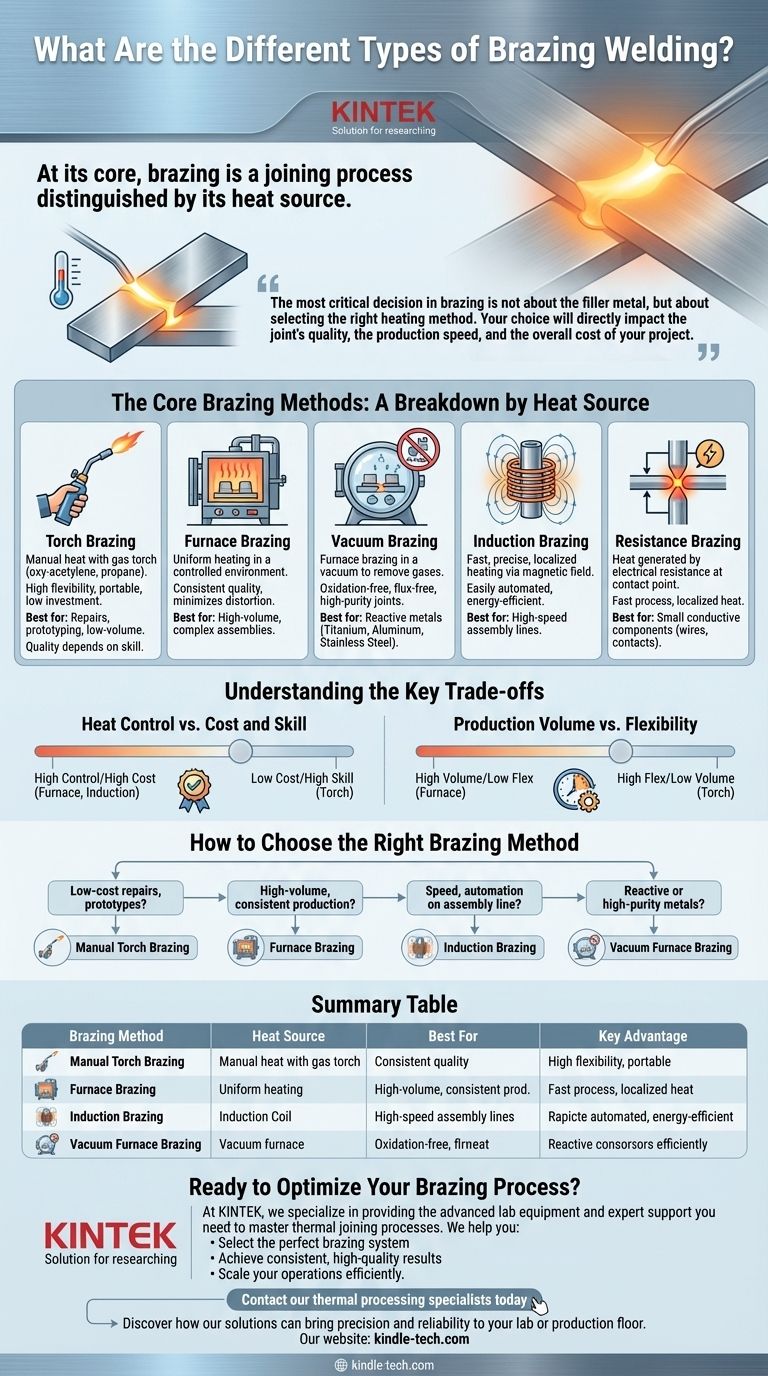
Im Kern ist das Löten ein Fügeverfahren, das sich durch seine Wärmequelle auszeichnet. Obwohl oft mit dem Schweißen verwechselt, verbindet das Löten Metalle mithilfe eines Füllmetalls, das bei einer niedrigeren Temperatur als die Grundmaterialien schmilzt, wodurch starke Verbindungen ohne Schmelzen der Teile selbst ermöglicht werden. Die primären Lötarten werden durch die Methode der Wärmezufuhr definiert, einschließlich Flammlöten, Ofenlöten, Induktionslöten und Widerstandslöten.
Die wichtigste Entscheidung beim Löten betrifft nicht das Füllmetall, sondern die Auswahl der richtigen Heizmethode. Ihre Wahl beeinflusst direkt die Qualität der Verbindung, die Produktionsgeschwindigkeit und die Gesamtkosten Ihres Projekts.
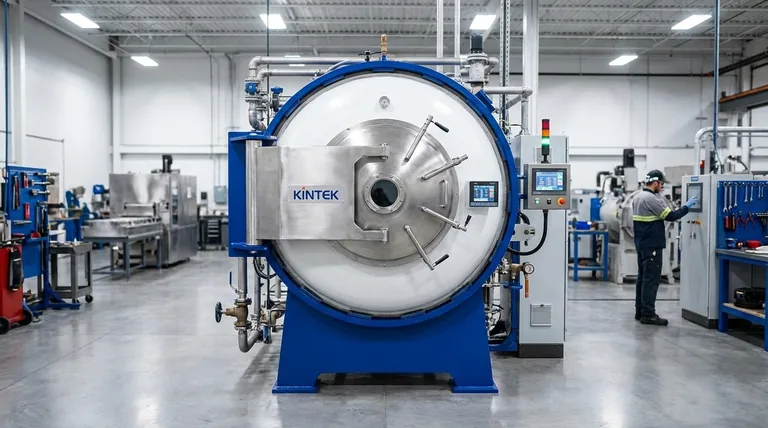

Die Kern-Lötmethoden: Eine Aufschlüsselung nach Wärmequelle
Lötmethoden werden fast immer danach kategorisiert, wie sie Wärme erzeugen und anwenden. Jeder Ansatz bietet ein einzigartiges Profil in Bezug auf Geschwindigkeit, Kosten, Präzision und Eignung für verschiedene Materialien und Produktionsmengen.
Flammlöten
Dies ist die gebräuchlichste und vielseitigste Form des Lötens. Dabei wird ein gasbetriebener Brenner (wie Acetylen-Sauerstoff oder Propan) verwendet, um die Teile manuell zu erhitzen und das Füllmetall in die Fuge zu schmelzen.
Es ist sehr portabel und erfordert eine geringe Anfangsinvestition, was es ideal für Reparaturen, Prototypenbau und Kleinserienfertigung macht. Die Qualität hängt jedoch stark von der Geschicklichkeit des Bedieners ab.
Ofenlöten
Beim Ofenlöten werden die Bauteile (mit vorplatziertem Füllmetall) in einen Hochtemperaturofen geladen. Die gesamte Baugruppe wird in einer kontrollierten Umgebung gleichmäßig auf die Löttemperatur erhitzt.
Diese Methode ist perfekt für die Großserienfertigung komplexer Baugruppen, da sie konsistente, hochwertige Verbindungen mit minimaler Verformung erzeugt. Sie gewährleistet, dass auch schwer zugängliche Fugen gleichmäßig erhitzt werden.
Vakuumlöten
Vakuumlöten ist eine spezielle Art des Ofenlötens. Der Prozess findet in einem Vakuum statt, das Sauerstoff und andere Gase entfernt, die die Metalle verunreinigen oder oxidieren könnten.
Dies ist unerlässlich für das Fügen reaktiver Metalle wie Titan, Aluminium und Edelstähle sowie für die Herstellung einer sauberen, flussmittelfreien Verbindung. Es ist ein Standard in der Luft- und Raumfahrt-, Medizin- und Halbleiterindustrie.
Induktionslöten
Diese Methode verwendet ein wechselndes Magnetfeld, das von einer Induktionsspule erzeugt wird, um die leitfähigen Metallteile zu erhitzen. Die Erwärmung ist extrem schnell, präzise und auf den Fugenbereich lokalisiert.
Induktionslöten lässt sich leicht automatisieren und ist hochgradig wiederholbar, was es zu einer Top-Wahl für Hochgeschwindigkeits-Montagelinien macht. Es ist auch energieeffizient, da es nur den Teil des Werkstücks erhitzt, der gefügt werden muss.
Widerstandslöten
Beim Widerstandslöten wird Wärme durch den elektrischen Widerstand der Fuge erzeugt, wenn Strom durch sie fließt, typischerweise über Kohleelektroden. Die Wärme konzentriert sich auf den Kontaktpunkt.
Es ist ein schnelles Verfahren, das sich zum Fügen kleiner, hochleitfähiger Komponenten eignet. Es wird häufig zum Anbringen von elektrischen Kontakten und Drähten verwendet, wo eine lokalisierte Erwärmung entscheidend ist.
Die wichtigsten Kompromisse verstehen
Die Wahl einer Lötmethode erfordert ein Abwägen konkurrierender Prioritäten. Das Verständnis dieser Kompromisse ist entscheidend für eine fundierte Entscheidung, die mit Ihren technischen und geschäftlichen Zielen übereinstimmt.
Wärmekontrolle vs. Kosten und Geschicklichkeit
Präzise Wärmekontrolle ist der wichtigste Faktor für eine hochwertige Lötverbindung.
Ofen- und Induktionslöten bieten eine außergewöhnliche, automatisierte Kontrolle, sind aber mit hohen Investitionskosten verbunden. Flammlöten ist kostengünstig, legt aber die Verantwortung für die Wärmeregelung vollständig in die Hände eines erfahrenen Bedieners.
Produktionsvolumen vs. Flexibilität
Ihre benötigte Leistung bestimmt Ihre Wahl. Ofenlöten ist für die Massenproduktion identischer Teile ausgelegt, ist aber für Einzelanfertigungen aufgrund langer Heiz- und Kühlzyklen sehr ineffizient.
Flammlöten bietet maximale Flexibilität für einzigartige Reparaturen oder Prototypen, kann aber die Geschwindigkeit und Wiederholbarkeit automatisierter Methoden für große Mengen nicht erreichen.
Material- und Atmosphärenreinheit
Die zu verbindenden Grundmaterialien können bestimmte Methoden sofort ausschließen. Viele hochfeste Legierungen und reaktive Metalle werden durch Sauerstoffexposition bei hohen Temperaturen geschwächt oder beschädigt.
Für diese Materialien ist Flammlöten keine Option. Eine kontrollierte Atmosphäre ist erforderlich, wodurch Ofenlöten im Vakuum oder mit einem Inertgas (wie Stickstoff oder Argon) die einzig praktikable Wahl ist.
So wählen Sie die richtige Lötmethode
Ihre spezifische Anwendung und Ihre Ziele werden Sie zur richtigen Methode führen. Verwenden Sie diese Richtlinien, um Ihre Optionen einzugrenzen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf kostengünstigen Reparaturen oder Einzelprototypen liegt: Manuelles Flammlöten bietet die beste Kombination aus Flexibilität und geringer Anfangsinvestition.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf hoher Stückzahl und konsistenter Produktion liegt: Ofenlöten ist der Industriestandard für die Herstellung zuverlässiger Verbindungen in großem Maßstab.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf Geschwindigkeit und Automatisierung an einer Montagelinie liegt: Induktionslöten bietet unübertroffene Geschwindigkeit und präzise, wiederholbare lokalisierte Erwärmung.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf dem Fügen reaktiver oder hochreiner Metalle (z. B. Titan, Edelstahl) liegt: Vakuumofenlöten ist unerlässlich, um Oxidation zu verhindern und die Integrität der Verbindung zu gewährleisten.
Letztendlich ist die Beherrschung der Auswahl Ihrer Wärmequelle der wichtigste Schritt zu einem erfolgreichen Lötprozess.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Lötmethode | Wärmequelle | Am besten geeignet für | Hauptvorteil |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flammlöten | Gasbetriebener Brenner | Reparaturen, Prototypenbau, Kleinserien | Geringe Kosten, hohe Flexibilität |
| Ofenlöten | Kontrollierter Ofen | Großserien, komplexe Baugruppen | Gleichbleibende Qualität, gleichmäßige Erwärmung |
| Vakuumlöten | Vakuumofen | Reaktive Metalle (Titan, Edelstahl) | Oxidationsfreie, hochreine Verbindungen |
| Induktionslöten | Elektromagnetische Induktion | Automatisierte Montagelinien | Schnelle, präzise, lokalisierte Erwärmung |
| Widerstandslöten | Elektrischer Widerstand | Kleine leitfähige Komponenten | Lokalisierte Wärme, schneller Prozess |
Bereit, Ihren Lötprozess zu optimieren?
Die Wahl der richtigen Lötmethode ist entscheidend für die Herstellung starker, zuverlässiger Verbindungen in Ihren Metallkomponenten. Bei KINTEK sind wir darauf spezialisiert, Ihnen die fortschrittliche Laborausrüstung und den fachkundigen Support zu bieten, den Sie benötigen, um thermische Fügeprozesse zu meistern.
Wir helfen Ihnen:
- Das perfekte Lötsystem auszuwählen für Ihre spezifischen Materialien und Ihr Produktionsvolumen
- Konsistente, hochwertige Ergebnisse zu erzielen mit präziser Temperaturkontrolle und Atmosphärenmanagement
- Ihre Abläufe effizient zu skalieren vom Prototypenbau bis zur Großserienproduktion
Ob Sie mit reaktiven Legierungen arbeiten oder automatisierte Lösungen benötigen, KINTEK verfügt über die Ausrüstung und das Fachwissen, um Ihre Lötfähigkeiten zu verbessern.
Kontaktieren Sie noch heute unsere Spezialisten für thermische Prozesse, um Ihre Projektanforderungen zu besprechen und zu entdecken, wie unsere Lösungen Präzision und Zuverlässigkeit in Ihr Labor oder Ihre Produktionshalle bringen können.
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- Vakuum-Wärmebehandlungs-Sinter-Hartlöt-Ofen
- Molybdän-Vakuumwärmebehandlungsöfen
- 2200 ℃ Wolfram-Vakuumwärmebehandlungs- und Sinterofen
- Vakuumwärmebehandlungsöfen mit Keramikfaser-Auskleidung
- Vakuum-Wärmebehandlungs- und Levitation-Induktionsschmelzofen
Andere fragen auch
- Was ist der Unterschied zwischen Schweißen und Vakuumlöten? Wählen Sie die richtige Fügetechnik für Ihr Projekt
- Was kostet ein Vakuumlötofen? Ein Leitfaden zu Schlüsselfaktoren und Investitionsstrategie
- Wofür wird ein Vakuumofen verwendet? Entdecken Sie Reinheit in der Hochtemperaturverarbeitung
- Was ist Löten im Rahmen der Wärmebehandlung? Erzielung überlegener Verbindungsqualität und Effizienz
- Können unterschiedliche Metalle hartgelötet oder hartgeschweißt werden? Ein Leitfaden für starke, zuverlässige Verbindungen



















