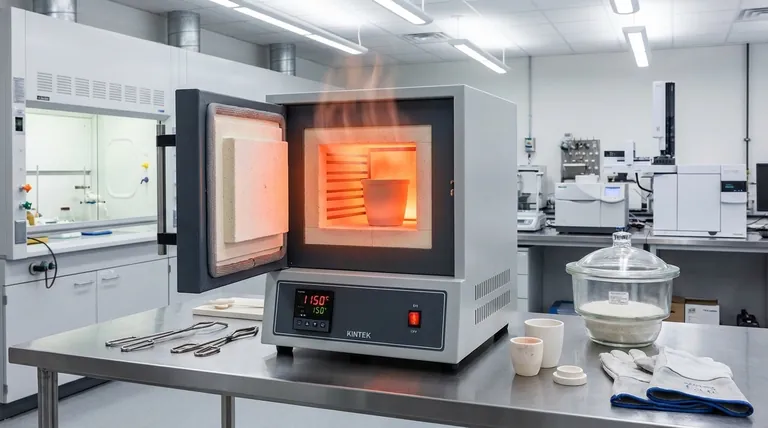
Im Wesentlichen ist ein Hochtemperatur-Muffelofen ein spezieller Ofen, der verwendet wird, um Materialien in einer streng kontrollierten und isolierten Umgebung auf extreme Temperaturen zu erhitzen. Diese Öfen sind unverzichtbar in Laboren, Forschungseinrichtungen und Industrieanlagen für eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen, einschließlich der Wärmebehandlung von Metallen (wie Glühen und Abschrecken), der Verarbeitung fortschrittlicher Materialien (wie dem Sintern von Keramiken) und analytischer Tests (wie dem Veraschen von Proben zur Bestimmung ihres anorganischen Gehalts).
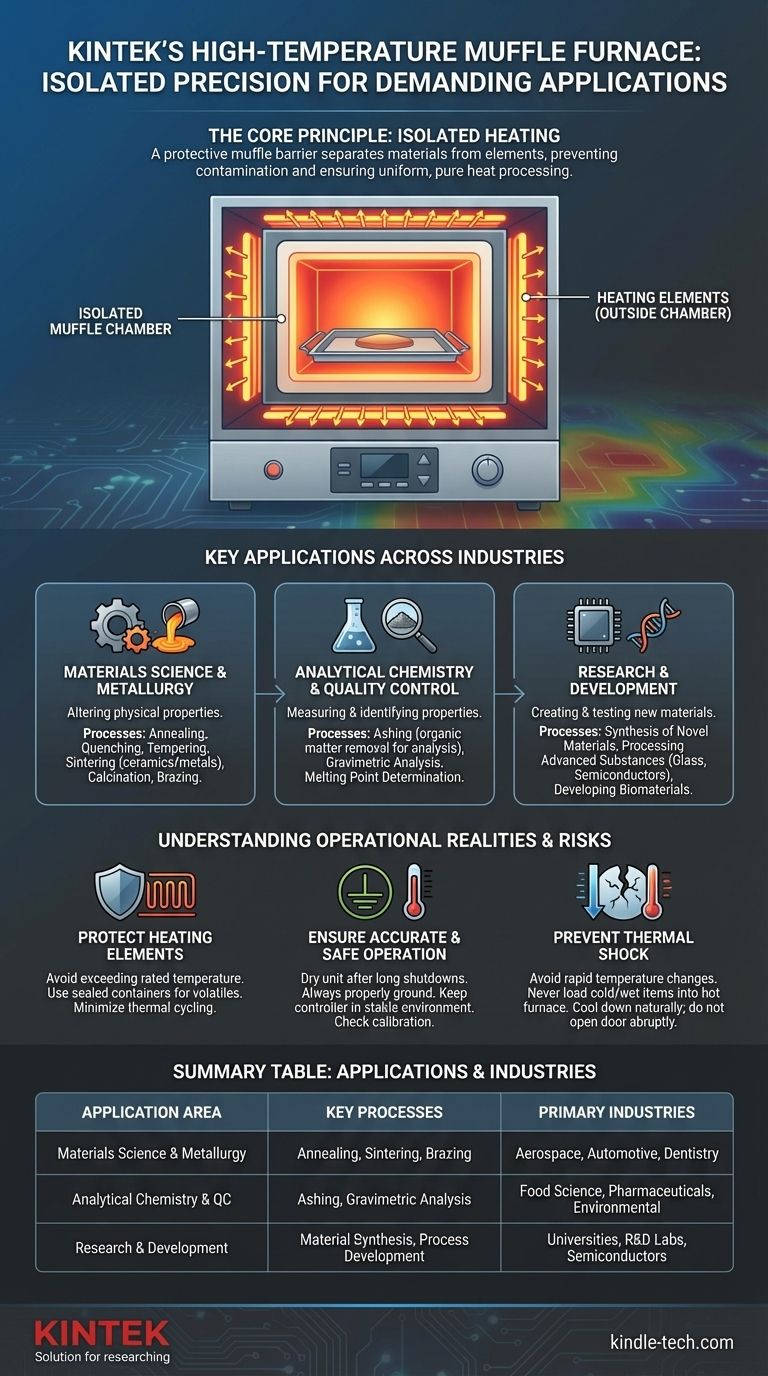
Das entscheidende Merkmal eines Muffelofens ist nicht nur seine hohe Hitze, sondern seine Methode der isolierten Erwärmung. Eine Schutzbarriere oder "Muffel" trennt das zu erhitzende Material von den Heizelementen, wodurch eine Kontamination verhindert und die Prozessreinheit und -konsistenz gewährleistet wird.

Das Kernprinzip: Isolierte Hochtemperaturverarbeitung
Um die Anwendungen des Ofens wirklich zu verstehen, müssen Sie zunächst sein grundlegendes Konstruktionsprinzip verstehen. Die "Muffel" ist der Schlüssel.
Was "Muffel" bedeutet
Der Begriff "Muffel" bezieht sich auf die isolierte Innenkammer des Ofens, die die Probe aufnimmt. Diese Kammer besteht typischerweise aus einem hochtemperaturbeständigen Keramikmaterial.
Die Heizelemente sind an der Außenseite dieser Muffel positioniert. Das bedeutet, dass die Wärme durch Strahlung und Konvektion auf Ihre Probe übertragen wird, aber die Elemente niemals direkten Kontakt mit der Probe oder ihrer unmittelbaren Atmosphäre haben.
Verhinderung von Kontamination
Diese Trennung ist der wichtigste Vorteil des Ofens. Sie verhindert, dass Verunreinigungen von den Heizelementen (wie abblätternde Oxide) oder Nebenprodukte der Brennstoffverbrennung (bei gasbefeuerten Modellen) die Probe verunreinigen.
Diese Reinheit ist in Anwendungen wie der analytischen Chemie, wo Spurenverunreinigungen die Ergebnisse ungültig machen würden, oder bei der Herstellung empfindlicher Elektronik und Biomaterialien unerlässlich.
Gewährleistung gleichmäßiger Wärme
Das geschlossene Design der Muffel fördert eine stabile und gleichmäßige thermische Umgebung. Es stellt sicher, dass die gesamte Probe gleichmäßig erhitzt wird, was entscheidend ist, um konsistente Materialeigenschaften bei Prozessen wie dem Glühen von Stahl oder dem Sintern eines Keramikteils zu erzielen.
Schlüsselanwendungen in verschiedenen Branchen
Die Fähigkeit eines Muffelofens, reine, gleichmäßige Wärme zu liefern, macht ihn in zahlreichen Bereichen unverzichtbar. Seine Anwendungen lassen sich in drei Hauptkategorien einteilen.
Materialwissenschaft und Metallurgie
Dies ist ein primärer Anwendungsfall, der sich auf die Veränderung der physikalischen Eigenschaften von Materialien konzentriert.
Gängige Prozesse umfassen die Wärmebehandlung von Metallen (Glühen, Abschrecken, Anlassen), das Sintern (Verschmelzen von pulverförmigen Materialien wie Keramiken oder Metallen zu einer festen Masse), die Kalzinierung (Erhitzen von Feststoffen zur Entfernung flüchtiger Substanzen) und das Hartlöten von Komponenten. Branchen von der Luft- und Raumfahrt bis zur Zahnmedizin verlassen sich auf diese Fähigkeiten.
Analytische Chemie und Qualitätskontrolle
In analytischen Umgebungen besteht das Ziel darin, die Eigenschaften eines Materials zu messen und zu identifizieren.
Die häufigste Anwendung ist das Veraschen, bei dem eine Probe bei hohen Temperaturen verbrannt wird, um alle organischen Stoffe zu entfernen. Dies ermöglicht es Technikern, die verbleibende nicht brennbare Asche genau zu wiegen, ein Standardverfahren in der Lebensmittelwissenschaft, der Wasserqualitätsanalyse und der Materialprüfung. Weitere Anwendungen umfassen Arzneimittelinspektionen und die Bestimmung des Schmelzpunktes von Asche.
Forschung und Entwicklung
Für Forscher ist der Muffelofen ein vielseitiges Werkzeug zur Herstellung und Prüfung neuer Materialien.
Er wird zur Synthese neuartiger Materialien, zur Verarbeitung fortschrittlicher Substanzen wie Glas und Halbleiter und zur Entwicklung neuer Biomaterialien eingesetzt. Seine kontrollierte Umgebung ermöglicht wiederholbare Experimente, die für den Fortschritt der Materialwissenschaft entscheidend sind.
Die operativen Realitäten und Risiken verstehen
Obwohl leistungsstark, ist ein Muffelofen ein empfindliches Gerät, das eine sorgfältige Bedienung erfordert, um Sicherheit, Genauigkeit und Langlebigkeit zu gewährleisten. Das Ignorieren dieser Realitäten kann zu beschädigten Geräten, ruinierten Proben und ungenauen Ergebnissen führen.
Schutz der Heizelemente
Die Heizelemente sind das Herzstück des Ofens und seine empfindlichste Komponente. Sie sind oft durch eine dünne Oxidschicht geschützt, die leicht beschädigt werden kann.
Sie müssen es vermeiden, die Nenntemperatur des Ofens zu überschreiten. Beim Erhitzen flüchtiger Materialien müssen diese in einem versiegelten Behälter platziert werden, um zu verhindern, dass Dämpfe die Elemente angreifen. Schließlich sollten häufige Abschaltungen minimiert werden, da thermische Zyklen die Elemente im Laufe der Zeit belasten und degradieren können.
Gewährleistung eines genauen und sicheren Betriebs
Verfahrensdisziplin ist unerlässlich. Der Ofen muss nach einer langen Abschaltung bei niedriger Temperatur (z.B. 200°C) getrocknet werden, um zu verhindern, dass Feuchtigkeit bei schnellem Erhitzen Schäden verursacht.
Aus Sicherheitsgründen muss das Gerät immer ordnungsgemäß geerdet sein. Für die Genauigkeit muss der Temperaturregler in einer stabilen Umgebung (typischerweise 0°C-40°C) gehalten und seine Kalibrierung regelmäßig überprüft werden.
Verhinderung von Thermoschock
Schnelle Temperaturänderungen können die Keramikmuffel des Ofens oder das zu verarbeitende Material reißen lassen. Legen Sie niemals einen kalten, nassen Gegenstand in einen heißen Ofen.
Lassen Sie den Ofen und seinen Inhalt nach Abschluss des Prozesses ebenfalls natürlich abkühlen. Ein abruptes Öffnen der Tür zum Abkühlen der Kammer kann irreparable Schäden durch Thermoschock verursachen.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihr Ziel treffen
Um dieses Wissen anzuwenden, gleichen Sie Ihr primäres Ziel mit den Kernfähigkeiten des Ofens ab.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf analytischen Tests liegt: Verwenden Sie den Ofen für präzises Veraschen, gravimetrische Analysen oder die Bestimmung der chemischen Eigenschaften von Materialien bei hohen Temperaturen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Materialherstellung oder Metallurgie liegt: Nutzen Sie seine Fähigkeiten zur Wärmebehandlung von Metallen, zum Sintern von Keramiken oder zum Hartlöten von Komponenten, wo Konsistenz und Reinheit von größter Bedeutung sind.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf Forschung und Entwicklung liegt: Der Ofen ist ein unverzichtbares Werkzeug zur Synthese neuer Materialien und zur Durchführung wiederholbarer Hochtemperaturexperimente in einer kontaminationsfreien Umgebung.
Das Verständnis, dass ein Muffelofen isolierte, gleichmäßige Wärme liefert, ist der Schlüssel zur Erschließung seines vollen Potenzials für präzise und zuverlässige Ergebnisse.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Anwendungsbereich | Schlüsselprozesse | Primäre Branchen |
|---|---|---|
| Materialwissenschaft & Metallurgie | Glühen, Sintern, Hartlöten | Luft- und Raumfahrt, Automobilindustrie, Zahnmedizin |
| Analytische Chemie & Qualitätskontrolle | Veraschen, Gravimetrische Analyse | Lebensmittelwissenschaft, Pharmazie, Umwelt |
| Forschung & Entwicklung | Materialsynthese, Prozessentwicklung | Universitäten, F&E-Labore, Halbleiter |
Benötigen Sie eine präzise, kontaminationsfreie Hochtemperaturverarbeitung? KINTEK ist spezialisiert auf hochwertige Laborausrüstung, einschließlich Muffelöfen, die für die anspruchsvollen Bedürfnisse von Laboren und Industrieanlagen entwickelt wurden. Unsere Lösungen gewährleisten die Zuverlässigkeit und Reinheit, die für Ihre kritischen Anwendungen in der Materialwissenschaft, analytischen Prüfung und F&E erforderlich sind. Kontaktieren Sie noch heute unsere Experten, um den perfekten Ofen für Ihre Ziele zu finden!
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- 1400℃ Muffelofen für Labor
- 1700℃ Muffelofen für Labor
- 1800℃ Muffelofen für Labor
- Hochtemperatur-Muffelofen für Laborentbinderung und Vorsintern
- Labor-Muffelofen-Bodenhub-Muffelofen
Andere fragen auch
- Welche PSA ist für einen Muffelofen erforderlich? Wesentliche Ausrüstung für Hochtemperatursicherheit
- Müssen Sie den sauberen Tiegel vor Gebrauch vorheizen? Vermeidung von thermischem Schock und Gewährleistung der Prozessgenauigkeit
- Was sind die fünf gängigen Wärmebehandlungsverfahren für Metalle? Beherrschen Sie die Prozesse für präzise Materialeigenschaften
- Was sind die verschiedenen Arten von Laboröfen? Finden Sie die perfekte Lösung für Ihre Anwendung
- Welche 5 Sicherheitsvorkehrungen müssen beim Erhitzen von Substanzen im Labor getroffen werden? Wesentliche Regeln für die Laborsicherheit



















