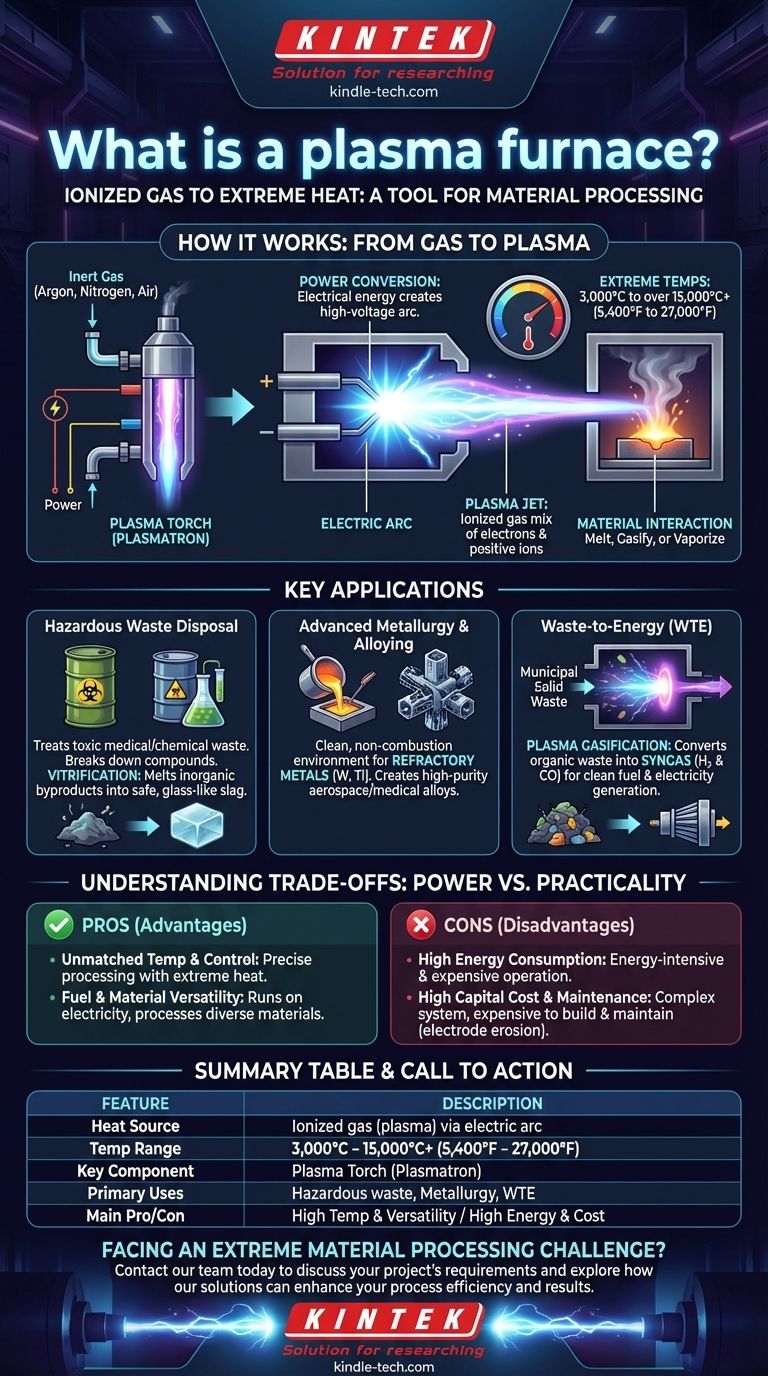
Im Kern ist ein Plasmaofen eine Industrieanlage, die einen Strom aus ionisiertem Gas – bekannt als Plasma – nutzt, um extrem hohe Temperaturen zu erreichen. Im Gegensatz zu herkömmlichen Öfen, die Brennstoff verbrennen, verwendet ein Plasmaofen Elektrizität, um ein Gas zu überhitzen und so einen kontrollierten, energiereichen Plasmastrahl oder Lichtbogen zu erzeugen, der in der Lage ist, praktisch jedes Material zu schmelzen, zu vergasen oder zu verdampfen.
Ein Plasmaofen sollte nicht nur als ein heißerer Ofen verstanden werden, sondern als ein grundlegend anderes Werkzeug für die Materialverarbeitung. Sein Wert liegt in seiner Fähigkeit, präzise kontrollierte Ultrahochtemperaturen ohne Verbrennungsnebenprodukte zu liefern, was ihn ideal für Aufgaben macht, die mit herkömmlichen Methoden unmöglich sind.
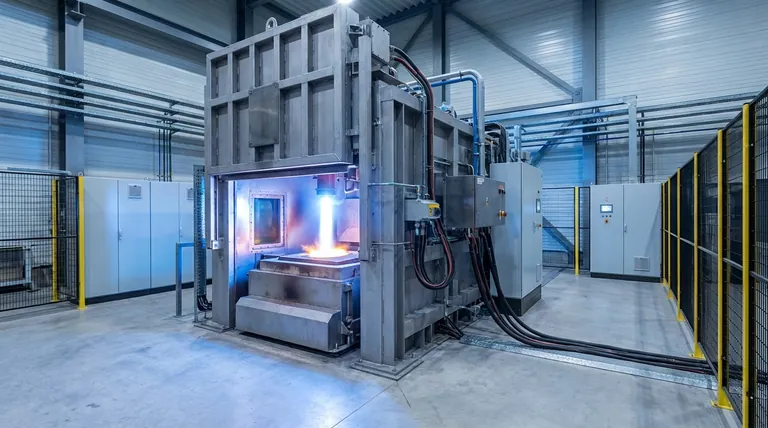

Wie ein Plasmaofen funktioniert: Von Gas zu Plasma
Der Betrieb eines Plasmaofens konzentriert sich auf seine Fähigkeit, einen stabilen Plasma-Lichtbogen zu erzeugen und aufrechtzuerhalten, der als primäre Wärmequelle dient. Dieser Prozess ist sauber, leistungsstark und hochgradig steuerbar.
Der Plasmabrenner: Das Herzstück des Systems
Die Schlüsselkomponente des Ofens ist der Plasmabrenner, manchmal auch Plasmatron genannt. Dieses Gerät ist dafür verantwortlich, elektrische Energie durch die Erzeugung von Plasma in thermische Energie umzuwandeln.
Erzeugung des Plasma-Lichtbogens
Im Inneren des Brenners wird ein Inertgas wie Argon, Stickstoff oder sogar Luft durch einen engen Kanal geleitet, der zwei Elektroden enthält. Zwischen diesen Elektroden wird ein Hochspannungs-Strom geleitet, der einen starken elektrischen Lichtbogen erzeugt.
Dieser intensive Lichtbogen reißt Elektronen von den Gasatomen ab, ein Prozess, der als Ionisation bezeichnet wird. Die resultierende Mischung aus freien Elektronen und positiven Ionen ist Plasma – ein eigenständiger Materiezustand.
Erreichen extremer Temperaturen
Während sich das Plasma bildet, erzeugt sein elektrischer Widerstand immense Hitze, wobei die Temperaturen im Lichtbogen zwischen 3.000 °C und über 15.000 °C (5.400 °F bis 27.000 °F) erreichen. Dies ist deutlich heißer als die Flamme in einem fossilen Brennstoffofen.
Materialinteraktion
Das überhitzte Plasma wird als Strahl oder Lichtbogen aus dem Brenner geleitet und auf das Zielmaterial gerichtet. Die intensive Wärmeenergieübertragung schmilzt, vergast oder verändert die Substanz in der Ofenkammer schnell chemisch.
Schlüsselanwendungen: Wo Plasmaöfen brillieren
Die einzigartigen Fähigkeiten von Plasmaöfen machen sie unverzichtbar für spezialisierte, hochwertige Industrieprozesse, die extreme Bedingungen erfordern.
Entsorgung gefährlicher Abfälle
Die Plasmatechnologie ist außergewöhnlich effektiv bei der Behandlung gefährlicher Abfälle, wie z. B. medizinischer Abfälle, Asbest oder chemischer Schlämme. Die extreme Hitze zerlegt komplexe toxische Verbindungen in ihre Grundelemente.
Der Prozess führt oft zur Vitrification, bei der anorganische Nebenprodukte zu einer stabilen, nicht auslaugbaren, glasartigen Schlacke geschmolzen werden, die Schwermetalle und andere gefährliche Materialien sicher immobilisiert.
Fortschrittliche Metallurgie und Legierungsherstellung
Plasmaöfen bieten eine saubere, verbrennungsfreie Umgebung, die ideal zum Schmelzen von hochschmelzenden Metallen mit sehr hohen Schmelzpunkten, wie Wolfram und Titan, ist. Diese Reinheit ist entscheidend für die Herstellung von Hochleistungslegierungen für die Luft- und Raumfahrt- sowie die Medizinindustrie.
Waste-to-Energy (WTE) Produktion
Bei der Verarbeitung von Siedlungsabfällen oder anderen organischen Materialien findet ein Prozess statt, der als Plasmagasifizierung bekannt ist. Die intensive Hitze zerlegt den Abfall in ein Synthesegas oder Syngas, das reich an Wasserstoff und Kohlenmonoxid ist und als sauberer Brennstoff zur Stromerzeugung genutzt werden kann.
Die Kompromisse verstehen: Leistung vs. Praktikabilität
Obwohl leistungsstark, ist die Plasmatechnologie keine Universallösung. Ihre Einführung wird durch eine klare Reihe von Vorteilen und erheblichen betrieblichen Herausforderungen bestimmt.
Vorteil: Unübertroffene Temperatur und Kontrolle
Der Hauptvorteil ist die Fähigkeit, Temperaturen weit über die Grenzen der chemischen Verbrennung hinaus zu erreichen. Diese Wärme kann durch Anpassen der elektrischen Eingangsleistung präzise gesteuert werden, was eine fein abgestimmte Materialverarbeitung ermöglicht.
Vorteil: Brennstoff- und Materialvielseitigkeit
Plasmaöfen sind brennstoffunabhängig und werden mit Strom statt mit bestimmten fossilen Brennstoffen betrieben. Sie sind auch materialunabhängig und können nahezu jede Art von Ausgangsmaterial verarbeiten, von festen Metallen bis zu flüssigem Schlamm.
Nachteil: Hoher Energieverbrauch
Die Erzeugung und Aufrechterhaltung von Plasma ist ein energieintensiver Prozess. Der hohe Stromverbrauch macht Plasmaöfen für Massenheizungsanwendungen deutlich teurer im Betrieb als herkömmliche Öfen.
Nachteil: Hohe Investitionskosten und Wartung
Plasmaöfen sind komplexe Systeme, deren Bau teuer ist. Die Elektroden im Plasmabrenner sind extremen Bedingungen ausgesetzt und erodieren mit der Zeit, was regelmäßige und kostspielige Wartung erfordert.
Die richtige Wahl für Ihr Ziel treffen
Die Wahl der richtigen thermischen Verarbeitungstechnologie hängt vollständig davon ab, das Leistungsbedürfnis mit den Betriebskosten in Einklang zu bringen.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Neutralisierung gefährlicher Abfälle liegt: Plasma bietet eine unübertroffene Wirksamkeit bei der Zerstörung toxischer Verbindungen und der Erzielung einer dauerhaften, sicheren Einkapselung durch Vitrifikation.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf der Herstellung hochreiner oder hochschmelzender Legierungen liegt: Die saubere, ultraheiße und kontrollierbare Umgebung eines Plasmaofens ist ein deutlicher technologischer Vorteil.
- Wenn Ihr Hauptaugenmerk auf dem Schmelzen von Massenmaterialien mit geringen Betriebskosten liegt: Ein herkömmlicher Verbrennungs- oder Elektrolichtbogenofen bleibt für die meisten Standardanwendungen die wirtschaftlichere und praktischere Wahl.
Letztendlich ist ein Plasmaofen ein Spezialinstrument zur Lösung extremer Materialherausforderungen, bei denen seine einzigartigen Fähigkeiten seine erheblichen Energie- und Kapitalinvestitionen rechtfertigen.
Zusammenfassungstabelle:
| Merkmal | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| Primäre Wärmequelle | Ionisiertes Gas (Plasma), erzeugt durch einen elektrischen Lichtbogen |
| Typischer Temperaturbereich | 3.000 °C bis über 15.000 °C (5.400 °F bis 27.000 °F) |
| Schlüsselkomponente | Plasmabrenner (Plasmatron) |
| Primäre Anwendungen | Entsorgung gefährlicher Abfälle, fortschrittliche Metallurgie, Waste-to-Energy (Vergasung) |
| Hauptvorteil | Unübertroffene Temperatur & Kontrolle; Brennstoff-/Materialvielseitigkeit |
| Hauptnachteil | Hoher Energieverbrauch und hohe Investitionskosten |
Stehen Sie vor einer extremen Herausforderung bei der Materialverarbeitung?
Wenn Ihre Arbeit die Neutralisierung gefährlicher Abfälle, die Herstellung hochreiner Legierungen oder die fortschrittliche Vergasung umfasst, könnten die einzigartigen Fähigkeiten eines Plasmaofens Ihre Lösung sein. KINTEK ist spezialisiert auf die Bereitstellung fortschrittlicher Laborgeräte und Verbrauchsmaterialien für anspruchsvolle Industrie- und Forschungsanwendungen.
Unsere Experten können Ihnen helfen, festzustellen, ob ein Plasmaofen das richtige Werkzeug für Ihre spezifischen Ziele ist. Kontaktieren Sie unser Team noch heute, um die Anforderungen Ihres Projekts zu besprechen und zu erfahren, wie unsere Lösungen Ihre Prozesseffizienz und Ergebnisse verbessern können.
Visuelle Anleitung
Ähnliche Produkte
- Hochtemperatur-Muffelofen für Laborentbinderung und Vorsintern
- 1800℃ Muffelofen für Labor
- 1700℃ Muffelofen für Labor
- 1200℃ Spaltrohr-Ofen mit Quarzrohr Labor-Rohröfen
- 1400℃ Muffelofen für Labor
Andere fragen auch
- Was ist der Verwendungszweck einer digitalen Muffelofen? Kontaminationsfreie Hochtemperaturverarbeitung erreichen
- Wozu dient ein Hochtemperatur-Muffelofen? Erreichen Sie eine reine, kontaminationsfreie thermische Verarbeitung
- Was ist der Zweck eines Laborofens? Präzise Hochtemperaturverarbeitung erreichen
- Was sind die Nachteile der Trockenasche? Wichtige Einschränkungen für eine genaue Elementanalyse
- Wie wirken sich Hochtemperaturöfen und Keramikschmelztiegel auf die Stabilität von Lithium-Ionen-Batterien aus? Master Precision Synthesis



















